What is Application-Aware Routing (AAR)?
| Application-Aware Routing is used by SD-WAN to prioritise traffic based on the application type and route traffic over specific network links. |
For many businesses, allocating network resources and prioritising specific applications is still a static setup. Utilising traditional Wide Area Network (WAN) solutions, the prioritisation of applications is defined by network administrators and then applied across all network edges, which may have different connectivity options available.
With the increased popularity of remote workforces and cloud service utilisation, businesses have increasingly moved towards Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) solutions, which introduce Application-Aware Routing (AAR).
In this article we’ll explain how AAR addresses the issues found in traditional WAN solutions and how it can be beneficial to your business.
The Problems Application-Aware Routing Solves
Traditional WAN networks typically utilise static path routing techniques, which limit networks to sending traffic over pre-defined paths. Regardless of the current traffic load on a given link, traditional WAN will continue to send traffic, which can be detrimental in the event links becoming overwhelmed. When this occurs, businesses can often experience degraded performance and even downtime.
This issue is only emphasised within WAN setups that cannot handle multiple transport links. These networks are limited by the capabilities of the single network link, which even with dedicated MPLS circuits may not provide the capabilities that business networks require. This can lead to slower, more expensive network routing, which is a waste of businesses resources.
Unfortunately, the latency and downtime that traditional WAN can experience often results in poor performance for the most critical applications, leaving businesses unable to efficiently complete day-to-day operations.
These issues have therefore led to SD-WAN introducing features such as dynamic path selection and Application Aware Routing, as it enables businesses to get more out of their network underlay, maximising network efficiency and minimising issues with downtime and latency.
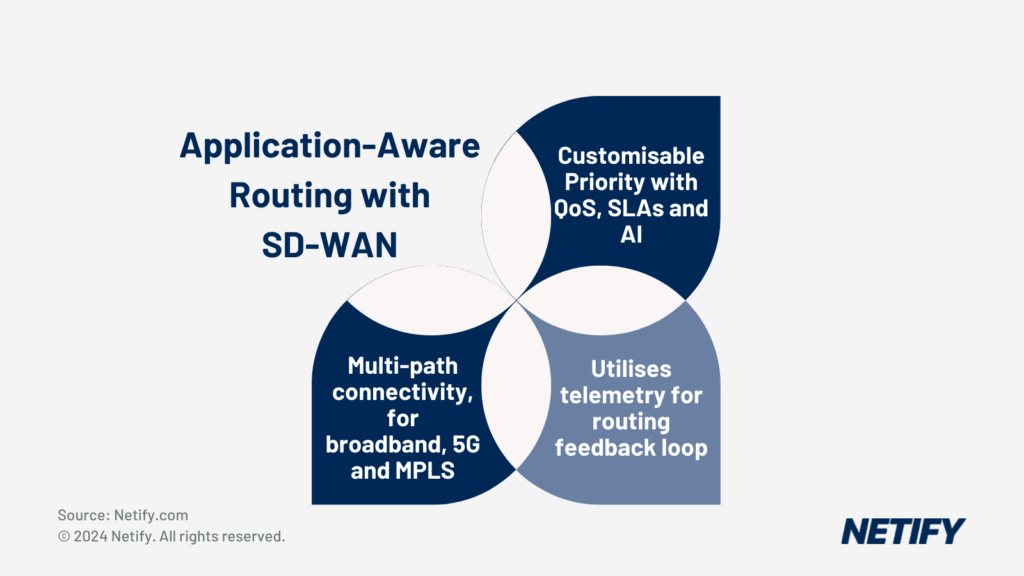
Core Functionality of AAR in SD-WAN
Application Aware Routing, within SD-WAN, offers businesses with the ability to prioritise critical applications based on real-time conditions and SLAs. AAR can evaluate telemetry from network connections using Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD), allowing for the SD-WAN solution to determine the best possible route at any given time. BFD pre-empts where issues may occur within the network and will suggest an alternate route when performance begins to degrade.
Alongside Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms, AAR can detect which applications are of higher importance to your business operations. These applications are then prioritised, allowing for critical applications to receive the bandwidth they need to perform.
Whilst telemetry does enable informed routing decisions, so can Service Level Agreements (SLAs). Businesses can set these SLAs for different traffic types, setting a maximum delay or amount of packet loss which SD-WAN has to abide by. AAR will automatically re-route the traffic in the event these SLAs are not being met. For businesses using leased lines and MPLS links that guarantee specific speeds, SD-WAN can also take these SLAs into consideration, with routing over these connections providing greater reliability due to these guarantees.
Dynamic Path Selection Mechanism in SD-WAN
Dynamic path selection enables both human-based and SD-WAN’s automated customisation of routing rules. Dynamic path selection forms a significant portion of AAR and allows for specification of low latency and greater control over critical applications. These ensure that applications, such as VoIP calls, are affected by minimal routing issues for improved networked operations.
Traditional solutions could emulate these path selection qualities through analysis of the port being used to transmit data. This rather outdated technique was solely reliant on traffic being routed across a commonly used port for applications, therefore making this solution less appropriate for businesses with proprietary systems or applications that use non-standardised ports. AAR, however, uses Deep Packet Inspection (DPI). DPI allows AAR to decrypt packets, with inspection helping to identify which application the packet is for. This method is far more flexible and efficient than port scanning, ensuring greater accuracy and connectivity of critical application traffic.
The Role of Performance Metrics in AAR Decisions
The telemetry utilised by the Application Aware Routing feature in SD-WAN indicates the quality of each path based on the following metrics: latency, jitter and packet loss.
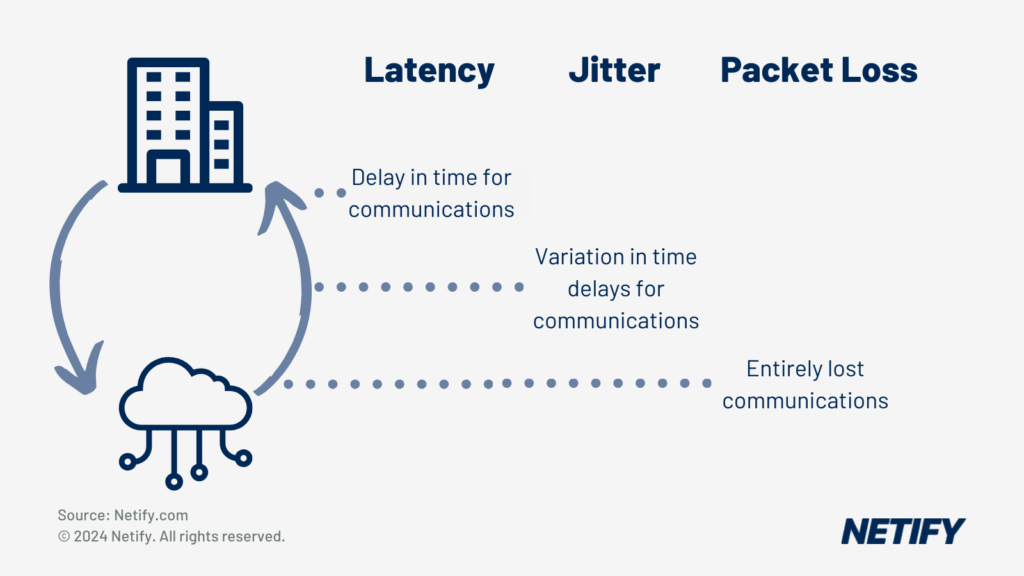
Network Latency refers to the round-trip time delay for data transmission between a source and destination within a network. This means that latency is measured from the point of initiation (e.g. a download link is clicked) to the point in which the response is received (file is downloaded).
Jitter refers to the variation in the flow rate of packet arrival times. Unlike latency, which refers to the overall delay of all packets, jitter refers to inconsistencies in delays between packets. Due to the rate of delay changing, jitter can introduce potential disruptions to business-critical real-time applications, such as Voice-over-Internet-Protocol (VoIP) and video conferencing.
Unlike latency and jitter, which are both related to timings of packets, packet loss refers to the complete loss of a packet. This can be due to a multitude of factors, such as collisions, malfunctioning network devices or high volumes of traffic. Whilst techniques such as Forward Error Correction (FEC) can assist in the process of resolving issues that arise from packet loss, avoiding packet loss entirely can be pivotal to ensuring critical business operations are not affected by delays or downtime.
Analysis of these metrics contribute to a feedback loop, with telemetry from selected paths helping AAR to determine how optimised routes are for applications.
AAR Configuration and Customisation
There are many forms of configuration and customisation for Application Aware Routing within SD-WAN. Network administrators can define SLA requirements for applications, ensuring that performance does not drop below a certain threshold and switching to a different connection in the event that it does. This means that critical applications such as video conferencing can be prioritised for low latency connectivity, whilst applications like file downloads can allow for delays due to being of lower importance.
These AAR settings are essential for businesses to fine tune the performance of their business network and ensures that they maximise the network connectivity for the most important business applications.
Benefits of Application-Aware Routing in SD-WAN
Fine tuning performance with AAR is beneficial as it optimised application performance for your business network. This ensures greater performance by utilising multiple paths and switching across the best performing link. For typically critical business applications, like video conferencing and cloud services, this means that businesses can experience fewer dropped calls, clearer video and faster application response times.
AAR within SD-WAN also provides businesses with improved link utilisation, which better distributes bandwidth to the right applications, meaning there is a more effective bandwidth split and gets the most out of each network connection. Businesses can benefit from this, as it enables greater utilisation of links such as broadband and 5G, meaning that there can be less reliance on more expensive connections (typically MPLS), offering a cost benefit to businesses
Businesses can also benefit from granular control over application performance. By being able to easily set the priority for specific applications and through SLAs, businesses can ensure that these applications are prioritised. Due to AAR leveraging DPI to understand the nature of each packet and its intended application, AAR is especially beneficial in comparison to traditional methods as it can require no manual adjustments, reducing network administrator workloads.
Conclusion
Application Aware Routing acts as an intelligent controller within SD-WAN solutions, continuously monitoring network telemetry and dynamically adjusting paths as part of a feedback loop to improve network performance. This means that critical applications are prioritised to receive the resources they need to perform.