What is Branch Office Connectivity?
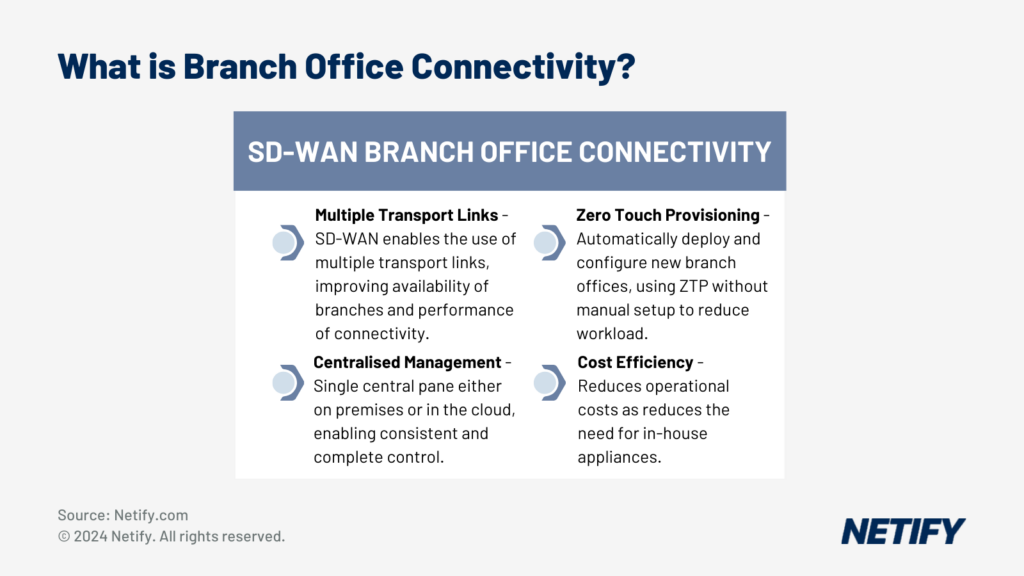
| To connect organisations that are spread over multiple branch offices, SD-WAN uses multiple transport links, centralised management, Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP) and improved cost efficiency. |
Large businesses are typically spread over multiple branches and so branch office connectivity is essential for operating a distributed enterprise. With traditional WAN networks, businesses found managing and optimising branch office connectivity particularly difficult due to the differences in available communication links and abundance of manual configuration processes required.
The process of managing branch office connectivity can be simplified by utilising Software Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) solutions. SD-WAN enables network administrators to manage all branch office connections through a single control panel, therefore reducing the overall network complexity and minimising the amount of manual configuration required at each branch office.
SD-WAN addresses other issues that traditional WAN branch offices face. SD-WAN provides the capability to optimise network performance by automatically routing its traffic via multiple paths based on current network conditions, application requirements and configured traffic priority policies. SD-WAN can offer built-in security features, such as segmentation and encryption, which reduce the need for dedicated on-premises appliances and lowers overhead costs for organisations.
Technological Overview
The SD-WAN virtual overlay network resides on top of transport links at the branch office. These transport links can include MPLS, broadband, LTE/5G. The virtual overlay abstracts the underlay physical network connections and intelligently routes traffic over the best performing traffic links in real-time, depending on application priority to the network. Over multiple branches, this provides networks with optimised inter-branch connectivity and reduces latency of shared applications and data between sites.
SD-WAN provides a single centralised pane for control and management of the network. This can either be hosted on-premises or based within the cloud (enabling remote access). This allows complete management of the entire SD-WAN fabric across all sites, with changes pushed out universally and reducing the need for manual changes at each branch site. In order to do this, the SD-WAN controller create secure tunnels with the SD-WAN edge at each branch office and pushes configurations and policies directly. By enabling network administrators to manage the entire network across multiple sites from one pane, SD-WAN reduces network complexity and reduces overall workload for administrators.
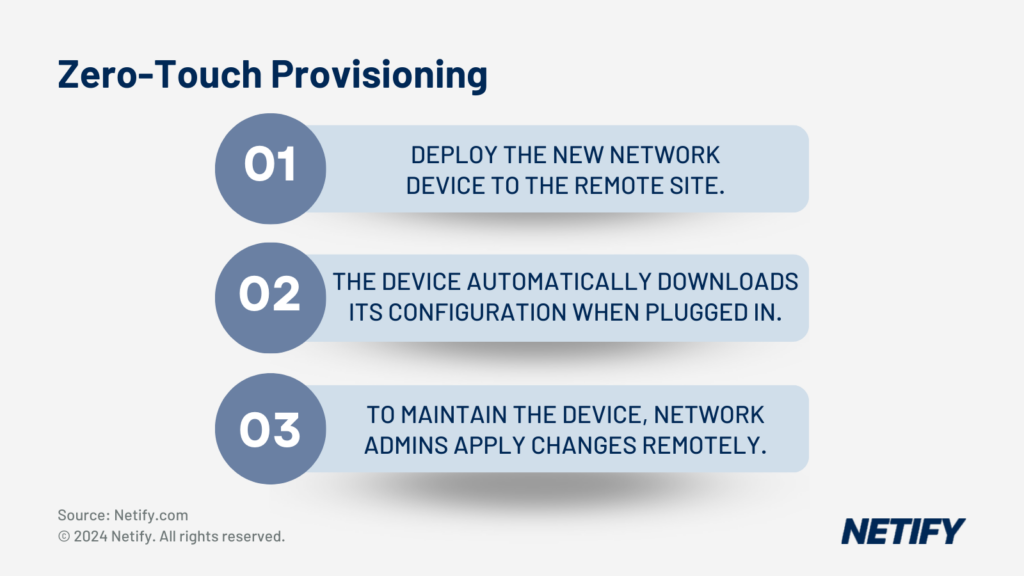
To reduce complexity of creating a new branch office, SD-WAN offers Zero Touch Provisioning capabilities. This means that branch offices can be automatically deployed and brought online without any on-site configuration. To do this, pre-configured SD-WAN edge appliances and shipped to branches and these automatically connect to the SD-WAN controller to receive configurations and policies. This reduces setup time and reduces manual work for network administrators.
Benefits of SD-WAN for Branch Office Connectivity
SD-WAN can leverage multiple communication links which includes typically more affordable broadband internet and cellular links. This reduces the reliance on dedicated MPLS circuits, which can be costly and thus SD-WAN reduces operational costs. To improve cost efficiency, SD-WAN can leverage multiple low-cost transport link and actively balance traffic load between each link using real-time traffic metrics and network conditions. When scaled across multiple branch offices, SD-WAN therefore minimises overall network costs.
By leveraging multiple routes, SD-WAN also enables automatic failover which prevents potential outages and minimises network interruptions. In combination with load balancing, the automatic failover capabilities improve network flexibility and resilience. By reducing network outages, this means that all branches are available at all times and resources can be shared which improves overall availability.
Application performance can be further enhanced by SD-WAN as it provides Quality of Service (QoS) policy management. This means that critical application traffic, such as Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and video conferencing applications, are prioritised and provided with adequate network resources to minimise any degradation of traffic. Changes to these policies are reflected across all branch offices, ensuring that all branches adhere to the same setup, regulations and reduces the need for individual changes of each branch site.
Challenges and Considerations
One challenge when implementing SD-WAN branch office connectivity is choosing the most appropriate SD-WAN vendor. The vendor selection process can be complex as different vendors provide different key offerings. Organisations must therefore factor the available features, cost and compatibility with existing infrastructure whilst also considering the potential use case over multiple branch offices. For example, organisations with a large volume of branch offices may prioritise scalability of the SD-WAN vendor.
Another consideration is that, whilst SD-WAN can leverage multiple communication links for flexibility and cost savings, each branch office may have differing available network links. This means that IT decision makers should consider the available links, their performance and plan the SD-WAN integration around these.
SD-WAN provides network segmentation capabilities, allowing the creation of isolated network segments based on user, device type or application. When combines with centralised security policies, this enables organisations to allow bring-your-own-device (BYOD) rules as users personal devices can use the network whilst isolated and separated from network resources, increasing security and minimising the potential for breaches.
Future Outlook and Innovations
One future outlook for branch office connectivity is that there will be an increased integration for cellular connectivity. This is significant for wireless links as it provides last-mile connectivity to branch offices that are more widespread. This assists branch offices with path diversity, failover and replaces wired links that may have aged and degraded, therefore improving network performance and reliability.
Many organisations are transitioning to ‘thin branches’. This means that network functions are commonly being hosted in the cloud rather than on-premises and provides greater flexibility for networks whilst also reducing cost of on-site appliances. As businesses become more reliant on cloud offered services, SD-WAN solutions continue to offer more visibility of application data and analytics, thus improving branch inter-connectivity troubleshooting and enables network administrators to optimise application performance.
Conclusion
Branch office connectivity is essential for operating a distributed organisation and is required for sharing of networked applications, data and traffic. Due to the complexity of differing network links and the scalability of managing all branches through a single control pane, SD-WAN offers a solution to reduce network complexity whilst also optimising network performance. SD-WAN also improves cost-efficiency, making it the optimal solution for connecting branch offices.