What is Cloud-Based SD-WAN?
A cloud-based Software Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) solution is a network overlay that enables businesses to leverage standard cloud capabilities such as instantly available scaling and a more powerful feature set. By abstracting the network control and management processes from the network hardware and allowing them to reside in the cloud, this provides network administrators with a centralised pane for SD-WAN orchestration and policy enforcement processes, which can not only reduce administrator workloads but can also help keep network enforcement consistency across different systems.
In recent years there has been a rapid increase in organisations leveraging SD-WAN solutions for their network architecture, with the expected annual growth of the global SD-WAN market to be around 31.9% through 2027, which is in no small part due to the emergence of cloud-based SD-WAN solutions.
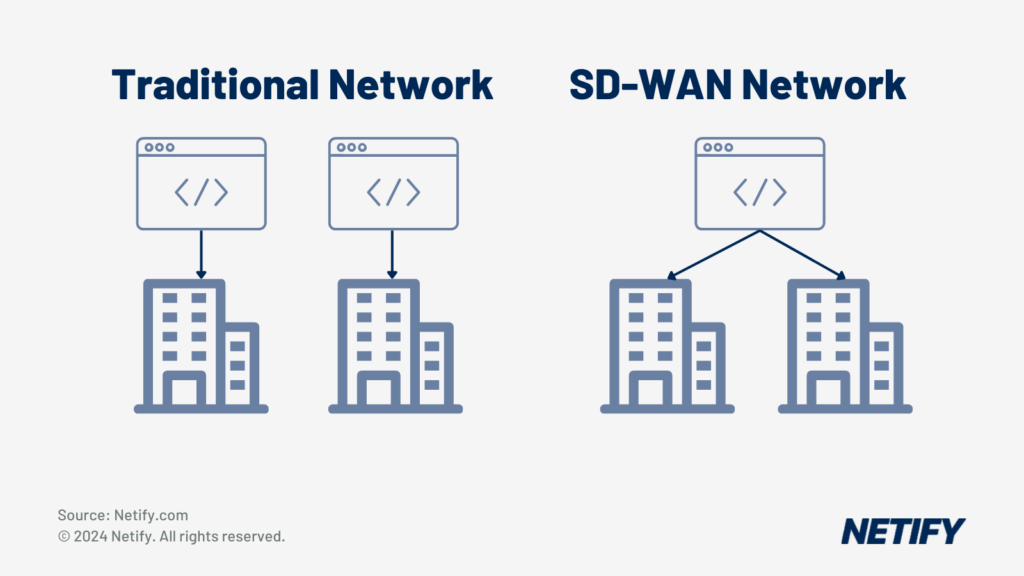
SD-WAN acts as a virtual overlay to the network, providing secure efficient connectivity between branch offices, data centres and cloud environments. By moving network management processes to the cloud, businesses enable greater agility and flexibility, whilst SD-WAN also offers greater cost-efficiency when compared to traditional on-premises networks. This is due to, when utilising cloud-based SD-WAN, organisations gaining the ability to leverage the cloud environments scalability.
By providing a central management panel, cloud-based SD-WAN enables a single interface for network administrators to interact with, set network policies and change configurations for all of the network. This reduces the need for individual on-site administrators and enables remote management, decreasing overall workload for managing the network and minimises the risk of human error at an individual site.
Hosting an SD-WAN solution in the cloud also provides further benefits, which includes features such as continuous cybersecurity updates, automated patching and threat detection.
Cybersecurity Enhancements in Cloud-Based SD-WAN
Continuous cybersecurity updates and automated patching of vulnerabilities are essential for businesses to proactively protect the network against the latest threats. By utilising cloud-based SD-WAN, networks can instantly switch to an updated threat detection mechanism in real-time, without any loss of security or any network outages, which can sometimes be experienced when using a traditional WAN network.
The automated patching of the SD-WAN solution also reduces the manual workload for network administrators, reducing the risk of human error, which could pose a threat to network security and ensures all devices receive the latest security fixes. The integration of advanced threat detection, such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) driven behavioural analysis and threat intelligence feeds, help networks to better identify and respond to potentially threat proactively, mitigating the threat before it can take effect.
Cloud-based SD-WAN can also integrate with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, which feed the network activity logs and security events into a single centralised SIEM platform and provides network administrators with real-time visibility into network activity, potential security incidents and enables rapid incident responses.
The granular segmentation capabilities offered by cloud-based SD-WAN allows orgs to isolate sensitive data and applications from less secure regions of the network. By creating separate virtual networks for different business units, applications or security zones, this minimises the attack surface and prevent lateral movement of threats.
Cloud-based SD-WAN enables and utilises strong authentication methods and practices, such as digital certificates and multi-factor authentication (MFA), which verify the identification before allowing connections. The communications between devices and the cloud is encrypted through industry-standard protocols such as IPsec and TLS, which ensures that sensitive configuration data and network traffic cannot be intercepted or tampered with by malicious actors.
Cloud Integration Capabilities
By basing the SD-WAN solution within the cloud, this provides the network with improved scalability, flexibility and cost-efficiencies. By scaling, cloud services can ensure SD-WAN solutions always have enough resources to cope with network strain but can also scale down to avoid unnecessary resources, which if the solution were not cloud-based, could result in either not enough networking appliances or too many when network utilisation varies. Cloud-based SD-WAN therefore offers a more cost-effective way of managing your business network, by only paying for the scale of operations you require.
For native integrations with Azure cloud services, cloud-based SD-WAN can automate deployments within Azure, simplifying the process of connecting branch offices to Azure-hosted applications and services. The most common use case for this is to establish secure connections between branch offices and the Azure Virtual Network (Azure VNet), which provides optimised application performance for Azure workloads. This integration also allows the implementation of consistent security policies across on-premises and Azure environments.
Integrations with Amazon Web Services (AWS) enable organisations to leverage the scalability and flexibility of AWS whilst maintaining the security and optimisation benefits of SD-WAN. Integrating AWS features, such as Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), enable business to extend their network SD-WAN fabric to AWS resources, which ensures the connection between branch offices and VPCs is secure and utilises optimised network routing for improved performance. This also implements consistent security policies and segmentation across the network for both on-premises and AWS.
The Google Cloud Platform (GCP), when integrated with cloud-based SD-WAN, enables automated provisioning and management of components from within GCP. This leverages the Google Cloud global network in order to provide optimised performance and advanced routing capabilities.
Access to Cloud-Based Backbones
Private backbones are a network of Points of Presence (PoPs), which interconnect across large geographical regions, many of which can be considered global PoPs due to their widespread coverage. These backbones provide high-speed, low-latency connectivity between points and can be accessed via a gateway. By routing SD-WAN traffic via a gateway, this bypasses public internet and leverages optimised routing. It should be noted that for first/last-mile transport (the link between the SD-WAN and the gateway) will often use public internet and so depending on the distance to the nearest gateway, may vary the reduction in latency.
Utilising a private backbone offers many benefits, one of which is improved performance. This is achieved through advanced routing protocols which are designed for optimised performance, compared to traditional broadband which is typically optimised for cost-efficiency. This helps to reduce latency, which can be essential to improve the overall user experience (UX). Private backbones also implement failover mechanisms which results in enhanced reliability and higher availability, whilst also providing scalability to accommodate fluctuating bandwidth demands and new sites.
One example of private backbones delivering improved performance reduced latency, when compared to public internet, is Cato Network’s private backbone. Testing showed that Cato’s private backbone reduced latency by 10% when transferring data between Singapore and Virginia, offering a significant improvement on traditional internet.
Comparison of Leading Providers Offering Private Backbone Access
Related Pages
Cloud-Based SD-WAN Comparison of Private Backbones
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Provider | Cato | Aryaka | VMware |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 04/11/2024 11:06 AM | hyelland | 04/11/2024 11:06 AM | Number of Worldwide PoPs | 80+ | 40+ | 200+ |
| 2 | hyelland | 04/11/2024 11:06 AM | hyelland | 04/11/2024 11:06 AM | Integration With Major Cloud Providers | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 3 | hyelland | 04/11/2024 11:06 AM | hyelland | 04/11/2024 11:06 AM | Backed SLAs | Yes | Yes | No |
| 4 | hyelland | 04/11/2024 11:06 AM | hyelland | 04/11/2024 11:06 AM | TCP Acceleration | Yes | Yes | No |
| 5 | hyelland | 04/11/2024 11:06 AM | hyelland | 04/11/2024 11:06 AM | Data Deduplication | Yes | Yes | No |
| Provider | Cato | Aryaka | VMware |
Innovations in Cloud SD-WAN
Cloud-based SD-WAN integrates Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to optimise network performance, enhance security and enable proactive management.
To provide improved network performance, AI is utilised to dynamically route traffic based on real-time network conditions, sending data via the best available path for each application. This is often paired with Quality of Service (QoS) policies and together, this minimises network congestion and maximises throughput. Dynamically routing with AI enables SD-WAN to mitigate changing demands and deliver consistent performance without disruption.
For many network administrators, managing the network can create a lot of work. Cloud-based SD-WAN goes some way to mitigating this issue by providing predictive analytics by leveraging machine learning. ML can anticipate potential network issues proactively and put measures in place before they can impact the network or its performance. Machine Learning algorithms achieve this by analysing historical network data and identifying patterns to provide predictive analytic forecasts for future network behaviour. This means that the SD-WAN can detect anomalies, predict when capacity upgrades are needed to accommodate future growth and where links may potentially be underperforming or failing.
Artificial Intelligence enhances threat detection by identifying and mitigating security threats in real-time. AI analyses network traffic and user behaviour, enabling the detection of anomalies or suspect activities which may indicate a potential breach. Examples of this could include spikes in data transfer to unknown destinations, where data exfiltration requires blocking. Abnormal behaviour patterns or deviations can indicate a threat, with analytics often assisting in the detection of subtle anomalies which otherwise would not be detectable by the human eye or traditional security tools. This includes threat indicators such as unusual login attempts, file access or resource usage.
Due to these benefits provided by the integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, we predict that there will be an increased focus on continuing to utilise AI algorithms to improve SD-WAN solutions.
One key emerging innovation for cloud-based SD-WAN is the integration of edge computing. Edge computing enables the processing of data closer to the source, which reduces the load on central cloud infrastructure and enables real-time decision-making. Edge computing optimises network performance and reduces latency, which is ideal for Internet of Things (IoT) integrations and real-time analytics.
Conclusion
Cloud-based SD-WAN solutions provide a network overlay that enables businesses to improve performance, security and management efficiency by abstracting the network control and management. This allows businesses to manage their networks remotely and reduces human error, whilst also enabling the automatic and continuous updating of cybersecurity features, patches and advanced threat detection for security against new-found vulnerabilities. Both integrations with cloud services and private backbones offer high-speed, low-latency connectivity and reliability in comparison to traditional broadband solutions. Finally, innovations in Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Edge computing integrations improve performance and security whilst also enabling proactive management, real-time analytics and IoT utilisation.