What is Cloud-Enabled SD-WAN?
| Cloud-Enabled SD-WAN is designed for organisations to use localised breakouts in order to more effectively use cloud applications. |
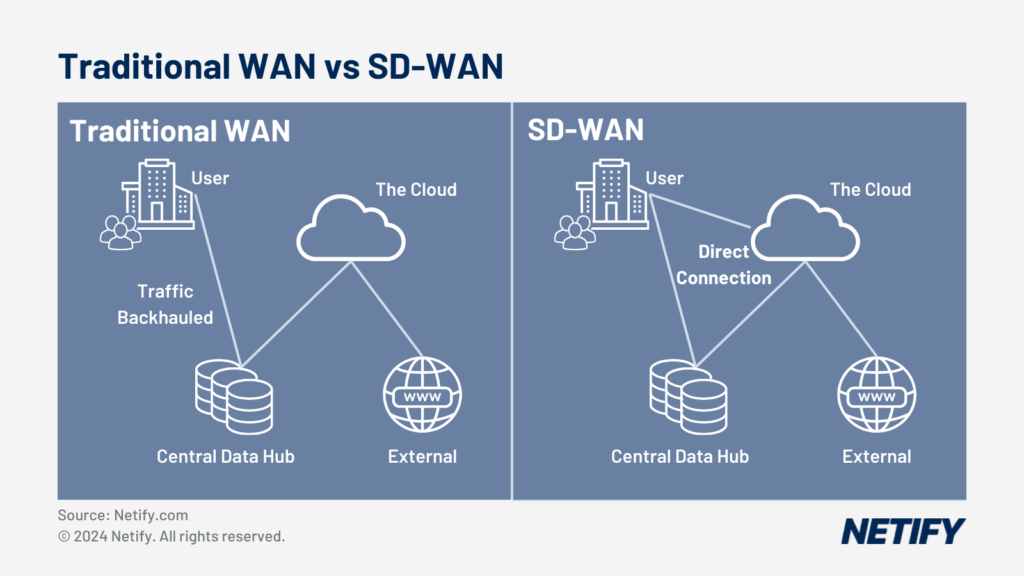
As the utilisation of cloud services within organisations is increasing, traditional enterprise network architectures have struggled to adapt to the changing requirements that using the cloud introduces. Software Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) solutions are an improvement on traditional WAN, enabling the growing reliance on cloud application services. SD-WAN provides seamless connections between branch offices, remote users and the cloud, with enhanced performance and security.
SD-WAN enables cloud connections via on ramping capabilities, creating a direct connection from branch offices to the cloud, reducing the need to backhaul data to a central data centre, as is used in traditional WAN solutions that make use of MPLS.
Due to the ability to create direct connections from users to the cloud, SD-WAN is therefore especially applicable in organisations utilising Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS).
As SD-WAN is cloud-centric, it decouples the network control plane and data plane, allowing for a centralised controller within the cloud for managing the SD-WAN, offering networks greater agility and flexibility.
Additionally, SD-WAN has the ability to dynamically steer traffic over multiple transport links including broadband and the cloud, allowing direct cloud access, the utilisation of multi-cloud to receive the benefits of different cloud providers, cloud-based security and cloud-based management.
Benefits of Cloud-Enabled SD-WAN
Cloud-enabled SD-WAN is better than traditional WAN as it provides enhanced performance, reduces costs and improves security.

By enhancing performance through real-time optimal network paths, SD-WAN reduces the latency, jitter and packet loss across the network. Cloud-enabled SD-WAN can utilise MPLS, broadband internet, 4G/5G, allowing it to be deployed in a range of locations. Some vendors of SD-WAN have introduced Forward Error Correction (FEC), where redundancy is introduced into packets, and packet duplication where packets are sent over multiple routes. These capabilities enhance the reliability and availability of the network and its applications.
By migrating from a router-based WAN system to a cloud-enabled SD-WAN, network administrators reduce the reliance on outdated MPLS systems, lower ownership costs and simplify the processes of deploying, managing and automating the network configuration.
Cloud-enabled SD-WAN offers integrated security, such as implementations of the SASE framework, Secure Web Gateway (SWG), Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS) which are all enforced via the cloud and therefore apply consistent policies regardless of location, device or access method.
Additional security features that can be found within SD-WAN include, but are not limited to, Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS), URL filtering, DNS-layer security, encryption, segmentation and id-based access.
These benefits provide businesses with enhanced agility and resilience against network issues.
Core Concepts of Cloud-Enabled SD-WAN
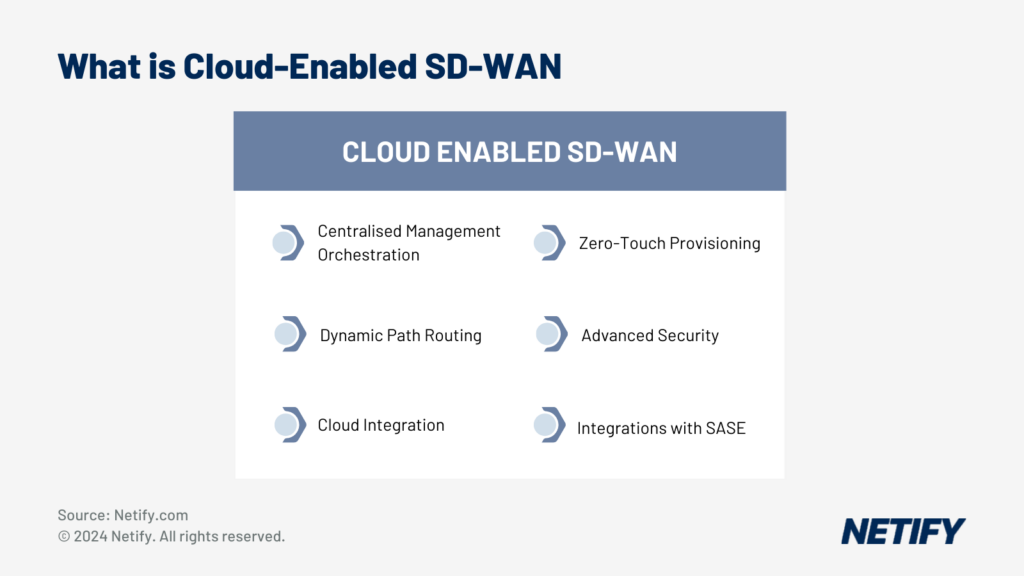
There are several core concepts to Cloud-Enabled SD-WAN:
Centralised Management
Cloud-enabled SD-WAN offers a centralised management system, allowing complete control and orchestration over the network via a single pane. This means that network administrators can manage policies, configurations and monitor performance all within a single unified management system. This reduces the need for manual configurations to be applied to individual devices, creating less network complexity and minimises the risk of human error. This also improves the simplicity and efficiency of the network architecture, whilst reducing overall complexity.
Dynamic Path Routing
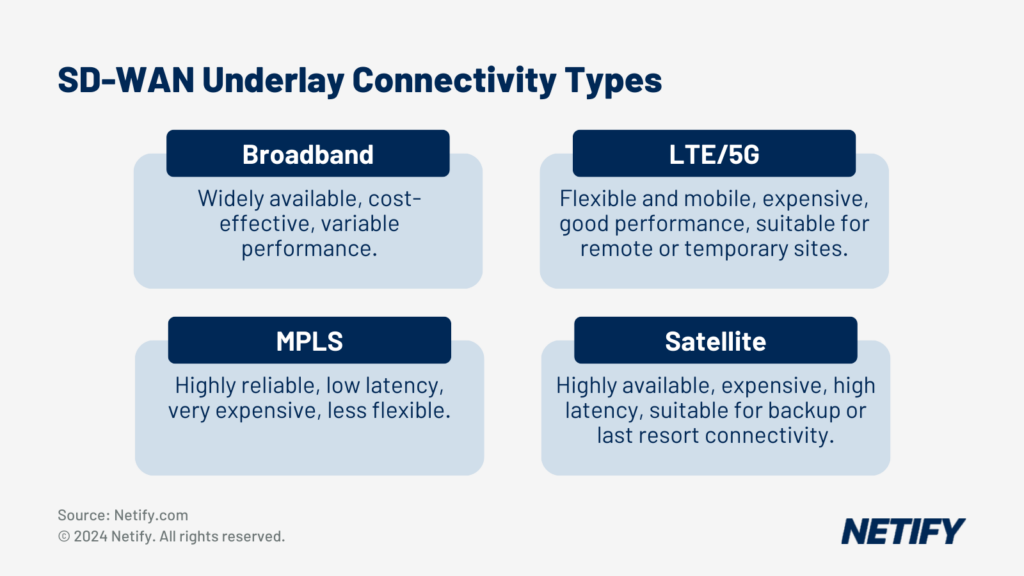
SD-WAN uses dynamic path routing over several network links such as broadband, LTE, MPLS and cloud routing in order to maximise performance. These can be combined to create a greater bandwidth and, by using real-time performance metrics SD-WAN can ensure the best path is used for critical applications. This application-aware routing capability is enhanced by the global visibility provided by the cloud-based controller found in cloud-delivered SD-WAN solutions, enabling more accurate path selection decisions.
Cloud integration
Cloud-delivered SD-WAN provides cloud-native integrations. These seamless cloud integrations for SD-WAN enable flexible and scalable network architecture, giving direct access to cloud applications through tunnelling and application-aware routing.
Zero-Touch Provisioning
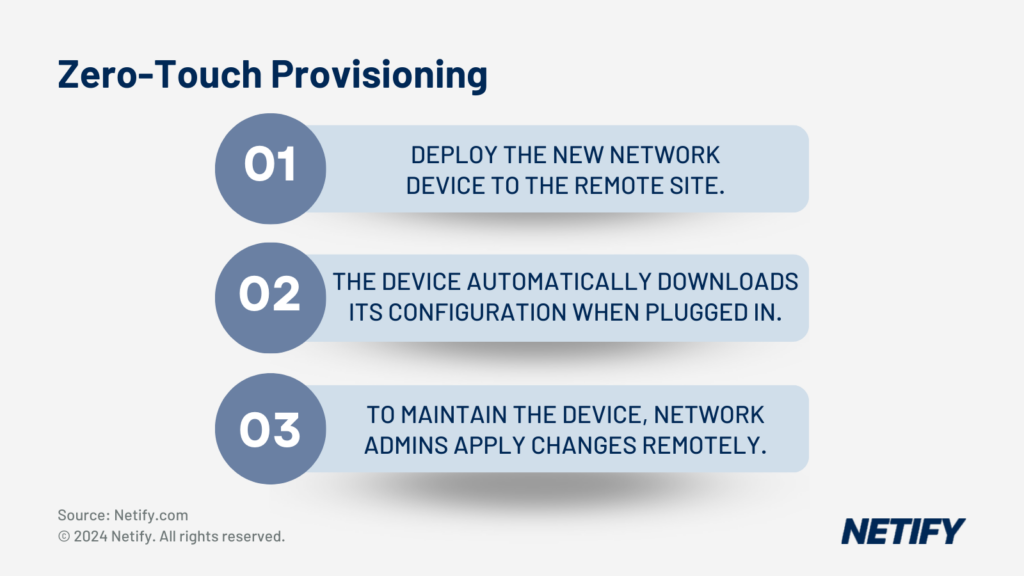
Another component of cloud-enabled SD-WAN is Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP), which allows for remote deployment of new SD-WAN devices, reducing the need for on-site technical expertise for manual configuration. Automated remote configuration of devices allows for rapid scaling and the ability of managing changing network requirements.
Security
SD-WAN also includes embedded security features such as firewalls, Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS), encryption and the enforcement of consistent policies for both cloud and on-premises environments. By utilising cloud with SD-WAN security features, these security features can be consumed as-a-service and reduces the need for dedicated appliances to cover these functions. A core principle of cloud-enabled SD-WAN is transparency in the visibility and control of cloud applications, allowing prioritisation of crucial applications for optimal performance and boosting overall user experience.
How Cloud-Enabled SD-WAN Works
SD-WAN monitors the health of network connections and traffic links to ensure that crucial applications are dynamically routed via the most reliable, high performing routes using real-time policies. The application-aware routing capability is enhanced by the global visibility provided by the cloud-based controller found in cloud-delivered SD-WAN solutions, enabling more accurate path selection decisions. The routing conducted by cloud-enabled SD-WAN is application-aware, optimising traffic based on granular Quality of Service (QoS) configurations, applying security policies and traffic shaping at a per-application level rather than a per-packet level.
On-Ramp capabilities are used for connecting to Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), with virtual overlays integrating direct connections to cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). This allows edge locations to optimise connections for low latency from enterprise locations to cloud applications without the need to backhaul traffic via a central data centre.
Integration with Public Cloud Providers
Cloud-enabled SD-WAN enables seamless integration and enhanced connections to major public cloud providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), providing the ability for global reach and advanced capabilities. These public clouds, through Points of Presence (PoPs), form a global backbone that increase cloud speed, reducing latency across the network, optimising transport of traffic whilst enterprises do not need to invest in their own global network backbone infrastructure. Additionally, through the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), SD-WAN can harness the cloud to provide insights and analyse network telemetry, providing actionable insights and scalable security for growing networks.
Amazon Web Services
Cisco's cloud-enabled SD-WAN Onramp allows for Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) to be implemented, providing connections to AWS via the Overlay Management Protocol (OMP) to the AWS transit gateway. This connection is optimised to provide high-speed connections to cloud applications.
Fortinet's cloud-enabled SD-WAN integrates AWS Transit Gateway Connect, which enables a direct connection to the AWS Transit Gateway, providing network users with a streamlined cloud experience.
Azure
Cisco's cloud-enabled SD-WAN integrates a Cloud Hub that uses Azure for its global backbone as an underlay to connect branch offices, data centres and virtual private clouds (VPCs).
Fortinet's cloud-enabled SD-WAN integrates Azure to provide virtual WAN (vWAN) to customers, allowing automated connections via virtual hubs and exchanging of routes through Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) or IPsec.
Google Cloud Platform
Cisco automates the creation of SD-WAN virtual routers within the Google Cloud Platform, the setup of site-to-cloud, site-to-site and Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) connectivity. Cisco also enables intent-based network policies across these virtual routers.
Private Cloud Solutions and SD-WAN
Private cloud solutions can be integrated with cloud-enabled SD-WAN to offer enhanced control, security and performance management over a network when compared to public cloud solutions. Both Aryaka and Cato have both developed systems to leverage private backbones with their cloud-enabled SD-WAN solutions.
Cato have developed a converged cloud-native SD-WAN solution that uses Cato’s own private global backbone. Cato’s private backbone consists of more than 65 Points of Presence (PoPs) worldwide, providing networks with optimised routing, built-in WAN optimisation and predictable performance across a range of different geographical locations.
This enables traffic optimisation and, with the Cato SD-WAN self-healing capabilities, provide reliable, end-to-end encrypted traffic:
The Cato software stack can be implemented with its backbone, meaning that for organisations there are no cost or complexity in building their own global backbone, whilst gaining the full security stack natively and a simplified way of deploying and managing a distributed network.
Aryaka cloud-enabled SD-WAN can also be integrated with its global layer 2 private backbone, which offers a suite of managed services, such as Aryaka’s SmartConnect functionality. SmartConnect offers SD-WAN connections SLAs, last mile management and additional optimisation features for increasing network performance.
By utilising a private cloud, networks limit the exposure of their infrastructure and cloud applications to the internet when compared to multi-tenant environments and this isolation of the cloud environment means that data is better encrypted with enhanced security and privacy. Private clouds also provide a greater level of control and can be custom to the specific requirements of enterprise needs and therefore changes are optimised for faster deployment. Using a private cloud also provides a more predictable global performance, due to not sharing resources with other tenants, gives consistent low latency, no variation of public internet, the ability for WAN optimisation and for cloud-edge connections to maximise end-to-end throughput. Private clouds can also reduce operational complexity, enabling simpler deployments and improving security of the network.
Challenges and Considerations
When considering cloud-enabled SD-WAN, IT decision makers must consider whether they wish to utilise a public or private cloud backbone and the implications this may have on their network.
A public backbone connects a cloud-enabled SD-WAN via a virtual gateway that is directly integrated with major public cloud providers, improving app performance and reliability compared to standard internet transport.
Alternatively, a private backbone, connecting organisations with the SD-WAN vendors nearest Point-of-Presence (PoP) will require traffic to traverse via the vendor's private network, which can lower latency, packet loss and jitter compared to public internet transport.
- As private backbones require SD-WAN vendors to provide dedicated distributed Points-of-Presence, this comes at a cost to the vendor and is thus usually reflected in the pricing to the customer.
- Private backbones provide an additional layer of isolation and protection since traffic is routed for a portion of the communication on the SD-WAN vendor's network. During this period, data does not traverse the public internet, therefore reducing the attack surface of the network, however it should be noted that data transmitted to a private backbone will still use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) until it reaches the private PoP. This means that private end-to-end connections are not possible, unlike with MPLS.
- Private backbones offer SLAs on availability, latency, packet loss and jitter since the SD-WAN vendor controls their private backbone. The vendors can optimise routing and quickly resolve issues. Public backbones rely on connectivity from internet providers which is 'best-effort'. While major cloud providers have extensive networks already built, the SD-WAN vendor has less control over end-to-end performance and points within public backbones may be prone to congestion.
- As multi-cloud is a popular trend, where networks leverage multiple cloud providers services, network administrators can deploy SD-WAN within AWS, Azure and Google Cloud Platform, routing traffic across each cloud providers backbone in order to gain high performance connections.
Future Trends and Innovations
An innovation is that Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly being used within cloud-enabled SD-WAN solutions to analyse historical data, predict potential network issues or threats and provide proactive fixes to ensure that there is no downtime. The ability to detect these issues in real-time provides an improvement on traditional human-monitored WAN systems and, through AI, SD-WANs are able to also automatically apply corrections to fix issues. By using big datasets, from analysing traffic over many organisations networks, AI is also capable of detecting zero day threats, through pattern matching and suspicious behaviour, previously impossible using human detection.
Another trend is the prominence of cloud-delivered Secure Access Service Edge (SASE), which include cloud-based SD-WAN solutions. SASE combines SD-WAN with security functions like secure web gateways (SWG), cloud access security brokers (CASB), firewall-as-a-service (FWaaS), and zero-trust network access (ZTNA) into a unified, cloud-delivered service, simplifying the network architecture by providing a single management system, with consistent policies enforcement. Due to being cloud-native, SASE (with cloud-delivered SD-WAN) enables scalability to organisations and reduces the complexity overhead on network administrators.
Conclusion
Cloud-enabled SD-WAN enhances network flexibility, performance, and security to distributed enterprise networks. SD-WAN also simplifies and optimises direct cloud access and multi-cloud usage through dynamic steering, whilst a unified central control pane provides improved and consistent network security features.
This means that SD-WAN provides a significant business impact, improves productivity for network users and administrators, reduces costs and complexity whilst also strengthening network security.