What is Link Aggregation?
| Link Aggregation combines multiple network links to create greater bandwidth availability. |
Businesses are typically transitioning from their traditional network solutions to Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) solutions due to performance-based incentives. One of the most compelling capabilities of SD-WAN is link aggregation, which combines multiple network connections into a single, more powerful link. Given that SD-WAN can utilise broadband, MPLS, cellular and satellite connections, the idea that these can be combined to create one link of superior ability highlights just how important link aggregation is to SD-WAN’s performance improvements.

In this article we’ll cover what Link Aggregation is, how it works and how organisations can leverage it to address their growing network demands.
Understanding SD-WAN Link Aggregation Mechanisms
There are several techniques that SD-WAN utilises to achieve Link Aggregation, all of which utilise SD-WAN’s ability to route over multiple network paths.
The first of these being Bandwidth Aggregation. By combining bandwidth across multiple different network links, businesses can create a larger, virtual connection to resources. This larger connection can be essential for delivering users access to bandwidth-intensive applications or resources. For example, video conferencing uses vast amounts of bandwidth for passing both video and audio across multiple sources, therefore by passing this through bandwidth aggregation, businesses enable the ability to reduce latency, desynchronised voices or even dropped calls.
Whilst bandwidth aggregation is an important feature for improving performance, for businesses concerned more about reliability, Flow Duplication is arguably more essential. Flow Duplication sends critical application traffic and data across multiple network links simultaneously, meaning that if one link fails or experiences a sudden surge in latency, the traffic will still reach its destination at the next-best rate. This means that businesses can ensure greater reliability of day-to-day operations, protecting against downtime for their most important systems.
Similar to flow duplication, flow balancing can also be used to send application traffic across multiple links. However, this technique differs as it distributes traffic based on a set of priorities that network administrators define, allowing for greater control of network link-usage, with different links being used for different priorities of application traffic. Flow balancing may be a preferable technique for your business if you have multiple systems that require flow duplication, as it allows your network administrators to plan which network links can be dedicated to each system, reducing the risk of flow duplication overwhelming a single link or each system’s traffic affecting one-another.
Finally, one of the more commonly known features of SD-WAN, is dynamic path selection. Dynamic path selection continuously monitors the network conditions via telemetry, identifying which links are underperforming or facing potential downtime. Once these are identified, SD-WAN can utilise path selection to route traffic via the most optimal network path for each packet of data, switching between links to constantly protect traffic from latency or downtime. This is a core feature for SD-WAN solutions, providing businesses with the ability to utilise multiple network paths effectively.
Key Features of SD-WAN Link Aggregation
The main feature that businesses will typically focus on from Link Aggregation is the improved performance that it provides. By aggregating multiple network links, SD-WAN can increase the bandwidth available to users, providing faster application performance.
Alternatively, through flow duplication techniques within link aggregation, businesses can also gain greater redundancy in their network. This ensures business continuity even if a primary network link fails.
However, these aren’t the only two benefits that link aggregation can offer businesses. Link aggregation can in fact be leveraged by businesses to reduce their network costs. By utilising less expensive broadband connections either alongside or in place of more expensive MPLS circuits, businesses can reduce costs whilst maintaining required performance.
Application Aware Routing (AAR), within SD-WAN, offers businesses with the ability to prioritise critical applications based on real-time conditions and SLAs. AAR can evaluate telemetry from network connections using Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD), allowing for the SD-WAN solution to determine the best possible route at any given time. BFD pre-empts where issues may occur within the network and will suggest an alternate route when performance begins to degrade. Alongside Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms, AAR can detect which applications are of higher importance to your business operations. These applications are then prioritised, allowing for critical applications to receive the bandwidth they need to perform.
When utilising multiple paths, businesses can also create improved connections to cloud resources. Due to certain paths being located closer to different cloud edges, this means that businesses can gain streamlined paths to all cloud systems.
Advanced Concepts in Link Aggregation
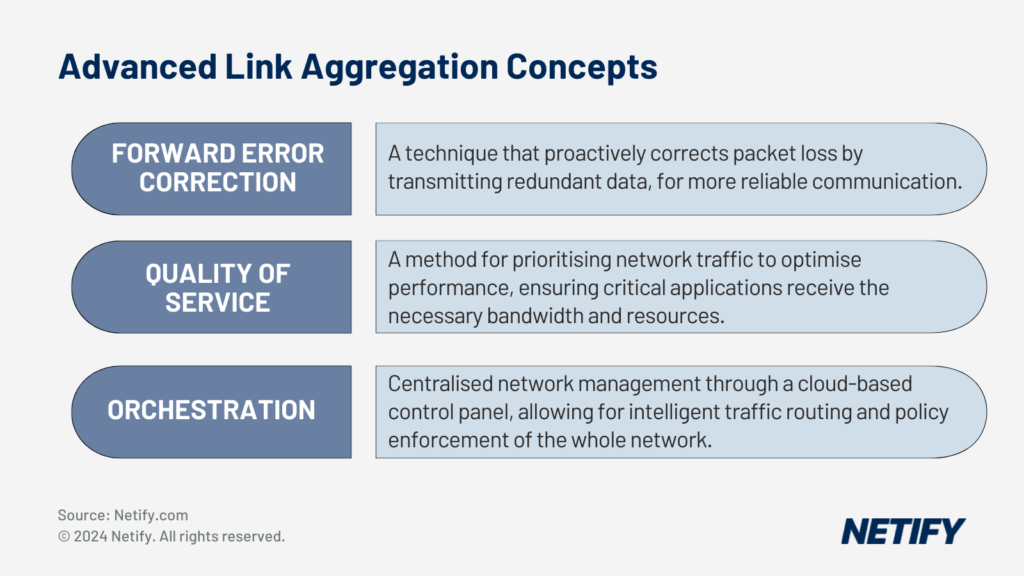
One advanced technique that enhances the performance of link aggregation is Forward Error Correction (FEC), which can assist in the process of resolving issues that arise from packet loss. FEC can be used to avoid packet loss entirely, which can be pivotal to ensuring critical business operations are not affected by delays or downtime.
Equally important is Quality of Service (QoS). QoS is a set of techniques to manage traffic across a network in order to optimise preferential performance. These optimisations vary between solutions but may prioritise specific network traffic, critical applications or services, allowing networks to increase reliability and maintain consistent performance. Techniques for QoS typically include traffic classification, queuing and scheduling in order to improve network efficiency. By increasing network efficiency, QoS reduces congestion and latency, whilst the overall user experience (UX) of the network is improved.
Another key offering is SD-WAN orchestration. SD-WAN provides a single, cloud-based control panel for managing all network connections and applying policies across the entire infrastructure. Application performance is optimised by SD-WAN orchestration through its ability to intelligently route traffic based on application requirements and network conditions. These enable dynamic path selection, QoS enforcement and application-aware routing and means that critical network applications are prioritised and given the necessary bandwidth to minimise latency, packet loss and jitter.
Benefits of SD-WAN Link Aggregation
Given the vast array of features that Link Aggregation utilises, these features provide businesses with many benefits.
The aggregation of multiple network links can increase your organisations total available bandwidth. This is particularly beneficial for businesses running data-intensive applications, such as cloud services, video conferencing, or large file transfers. By giving your business greater bandwidth, vital applications can run with greater efficiency and improved overall productivity and user satisfaction.
Another benefit is the redundancy measures that SD-WAN link aggregation can provide. With multiple network connections, the failure of one or more links does not necessarily result in downtime. SD-WAN can then automatically re-route traffic through other routes, ensuring operations are minimally affected. This level of reliability is particularly important for industries where downtime can result in significant revenue losses, such as within retail or financial services.
Businesses can also leverage link aggregation in order to save on network costs. Traditionally, businesses have relied on expensive dedicated circuits like MPLS to ensure network performance. SD-WAN link aggregation allows organisations to supplement or replace these costly circuits with more affordable broadband or cellular connections. By using a combination of low-cost options without sacrificing performance, businesses can reduce their overall network expenditure while still achieving high levels of reliability and performance.
Through the Application-Aware Routing features that are used by link aggregation, SD-WAN enables network administrators to prioritise critical applications. Applications such as Voice-over-Internet-Protocol (VoIP), video conferencing and financial transactions can be provided with priority over other traffic, improving performance for the most important business operations.
Practical Use Cases with Case Studies
There are many applications for SD-WAN’s link aggregation capabilities, with support for businesses of all sizes. Whether businesses need to improve performance for branch connectivity, remote worker support or even IoT integrations, SD-WAN link aggregation can be utilised to help improve your network.
Enterprise Branch Connectivity
Navigant Credit Union was struggling to expand their traditional WAN network across multiple branches. They were facing challenges with high operational costs, limited bandwidth availability and unreliable connectivity between branches. By adopting an SD-WAN solution, Navigant Credit Union were able to implement link aggregation to combine their MPLS and broadband connectivity. This helped to increase their bandwidth availability and improved connectivity by reducing network congestion and outages. They also found that by utilising broadband, Navigant were able to minimise extra costs, therefore helping to alleviate the high operational costs they were experiencing.
Remote Workforce Support
A global financial services company needed a way to provide secure, high-performance connectivity to its remote workforce, especially with the rise in remote work over the past few years. Their traditional network infrastructure was insufficient, lacking the flexibility and bandwidth optimisation needed to handle the volume of remote users. The financial services company were able to resolve this issue by utilising SD-WAN, with its link aggregation capabilities allowing broadband and 5G to be combined, providing more reliable connectivity to remote workers. Further to this, due to the in-built ZTNA capabilities within SD-WAN, the financial services company were able to safeguard sensitive financial data, even with users dispersed remotely.
Assisting with Limited Bandwidth
Destination Hotels & Resorts are a hospitality organisation with over 30 different hotels and locations across the United States. Unfortunately, due to their locations often being so remotely distributed, many of their network connections were limited only to very slow T-1 links. This meant that users staying at the hotels couldn’t effectively use the network for streaming or video conferencing, decreasing user satisfaction and deterring both personal and business trips from using the network. By introducing Peplink SD-WAN, Destination Hotels & Resorts were able to use balance series routers to aggregate multiple network links, such as DSL, fibre and LTE. This provided their customers with better bandwidth across their properties and improved their customer experience.
Internet of Things (IoT) Deployments
A smart manufacturing facility deployed thousands of IoT sensors across its production lines to monitor equipment performance, track inventory, and manage real-time data collection. However, the facility faced connectivity challenges due to the sheer number of devices transmitting data simultaneously. Network outages or delays in data transmission could lead to operational inefficiencies and potential production stoppages. By utilising SD-WAN link aggregation, the manufacturer was able to combine their broadband connectivity with LTE in order to improve traffic flow from the production line sensors to their central analytics platform.
Implementation Strategies
Business wanting to make full use of SD-WAN’s link aggregation should consider multiple factors.
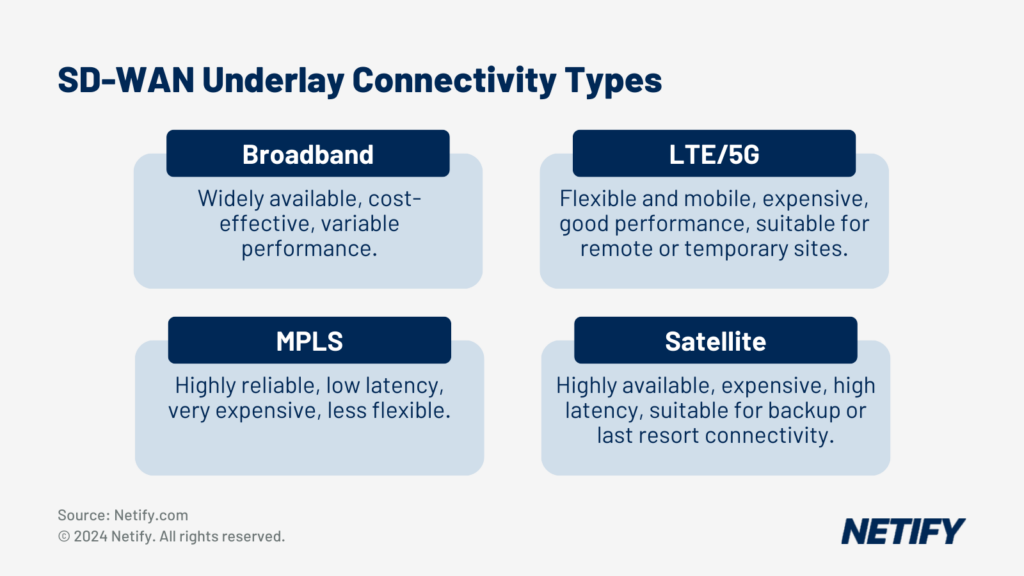
The first of these is their network underlay. Network underlay refers to the network links, such as broadband internet, cellular and MPLS connections. The more varied the available link types, the more beneficial SD-WAN’s link aggregation can be. Limited connectivity may mean that businesses are unable to route traffic effectively, therefore emphasising the importance of making sure that there are an appropriate number of connections available and that these are of diverse types.
Another factor that organisations must consider is the requirements of their applications. By understanding the performance needs of business-critical applications, network administrators can set effective Quality of Service policies in order to ensure that the most important applications are prioritised.
Future Outlook
Whilst link aggregation is becoming a more common feature in SD-WAN solutions, the changes in network underlay technologies are increasing link aggregation capabilities. The introduction of 5G networks has provided businesses with access to faster, more reliable network links and we can only anticipate that this will continue to improve link aggregation with future revision of cellular connections.
In addition to network underlay changes, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been introduced for many features within SD-WAN. With AI being increasingly adopted for dynamic path selection algorithms, it enables SD-WAN to achieve more efficient traffic management.
Conclusion
Link Aggregation is an essential feature for SD-WAN solutions. By leveraging aggregation, businesses can combine multiple network links and apply intelligent traffic management techniques in order to enable greater performance and reliability. Whilst there are current significant benefits for day-to-day operations, we can only expect these benefits to increase due to the improvements in network underlay and the introduction of AI.