What is SSE?
| Secure Service Edge (SSE) solutions combine Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS), Secure Web Gateway (SWG) and Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA). |
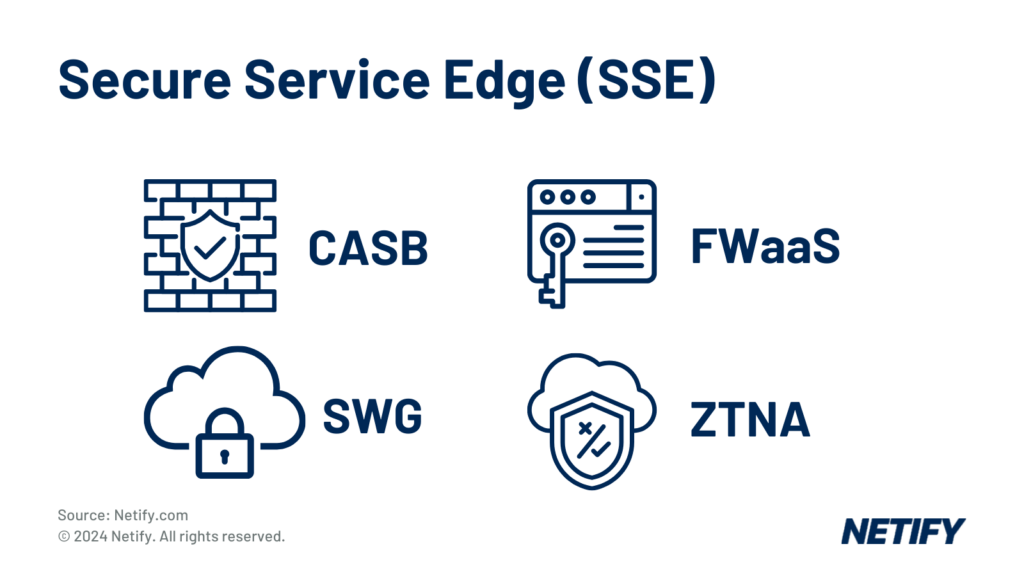
- Secure Service Edge (SSE) Features
Security Service Edge (SSE) is a component of Secure Access Service Edge (SASE). A common misconception is that SSE and SASE are the same thing, however SSE is primarily focused on network security, secure access and the protection of data, unlike SASE which combines SSE with SD-WAN to provide networks with performance optimisations, thus providing a holistic network solution.
Security Service Edge comprises of many security features in order to ensure protection of the network through consistent policies across users and devices regardless of location. Features such as Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), Zero-Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS) enable Zero Trust policies to be implemented and reduce the need for traditional data centre appliances.
SSE has been recognised as a separate market segment by Gartner, resulting in the market's own magic quadrant, indicating the technologies rise in importance. The ability to decouple the network and security is being more frequently adopted by organisations, reducing the risk of leveraging disparate solutions and ensures that, through the use of a single vendor, the multiple security capabilities are bundled together via a cloud-centric model for ease of integration.
SSE's Role Within SASE
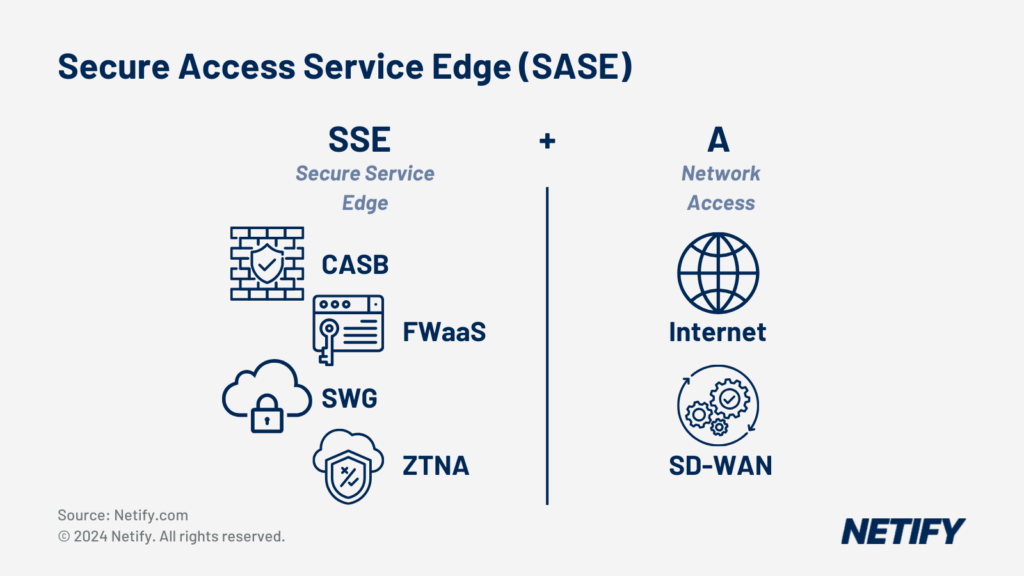
- Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) is SSE + SD-WAN (Access).
SSE’s role within SASE is that it primarily focuses on the security aspect of the SASE framework. SSE integrates security functions such as:
Related Pages
SSE Functions & Benefits
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Security Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 04/11/2024 09:49 AM | hyelland | 04/11/2024 09:49 AM | Secure Web Gateway (SWG) | Filters unwanted software/malware from network traffic and enforces regulation and policy compliance. |
| 2 | hyelland | 04/11/2024 09:49 AM | hyelland | 04/11/2024 09:49 AM | Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) | Grants users minimum access and requires authentication and continuous validation for system access. |
| 3 | hyelland | 04/11/2024 09:49 AM | hyelland | 04/11/2024 09:49 AM | Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) | Service that sits between cloud services and users to monitor activity and enforce policies. |
| 4 | hyelland | 04/11/2024 09:49 AM | hyelland | 04/11/2024 09:49 AM | Remote Browser Isolation (RBI) | Isolates browsing activity from endpoints and networks by executing web sessions on a remote server. |
| 5 | hyelland | 04/11/2024 09:49 AM | hyelland | 04/11/2024 09:49 AM | Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS) | Cloud-based firewall, removing the need for on-premises hardware. |
| Security Function | Benefit |
SASE then integrates SSE as part of its solution with SD-WAN, providing users with a holistic network management tool, leveraging a combination of security and network performance benefits.
Technological Innovations and AI in SSE
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is being increasingly adopted within SSE solutions for threat detection and automated response. To implement this functionality, artificial intelligence is used to analyse patterns and behaviours of user and application traffic in order to predict potential breaches. Adaptive threat protection automatically identifies these threats in real time, mitigating risks before they can cause any issues.
Cloudflare, a 2024 Gartner SSE Magic Quadrant leader, leverages both Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (ML) in order to provide Zero Trust Access control product, through Cloudflare Access. Cloudflare access uses AI to monitor network behaviour, detecting anomalies and indicate potentially compromised accounts or insider threats.
The utilisation of artificial intelligence for security is an important innovation, a report by Cisco highlighted that AI-based systems could identify and categorise threats 60% faster than traditional methods. By improving threat response times, the overall user experience (UX) is improved and the workload for network administrators is decreased.
Benefits of SSE
Within modern businesses there is an evident shift to distributed workforces, with many businesses operating either an entirely remote or hybrid working environment. Security Service Edge benefits both remote and hybrid workforces as it enables comprehensive security for all users, devices and applications regardless of their location.
SSE provides multiple security functions via a single platform and thus reduces the risk of businesses having gaps in their security systems. This improves overall network security coverage and reduces the areas where potential threats may breach. This is important for maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of networks; therefore, SSE offers a single solution to cover large proportions of the network security.
By streamlining security and utilising a central policy management system, SSE enables organisations to ensure compliance to regulations by providing consistent security enforcement. This means that, should network administrators need to make changes to comply with regulations or company policies, these changes are rapidly deployed and will affect all devices in the exact same way, reducing the potential for human error where manual configuration was previously required.
SSE also offers a potential cost reduction. By moving away from traditional on-premises hardware and appliances, a cloud-delivered SSE solution can reduce the initial overhead to purchase appliances whilst also minimising costs to maintain and update on-premises infrastructure.
Due to the benefits supplied by Security Service Edge, Axis reported that it is believed that 82% of organisations are expected to have adopted SSE by 2025. This indicates the market is growing and that SSE is becoming more and more important to business networks.
Implementation Considerations
When implementing SSE there are several considerations for businesses. Firstly, IT decision makers should consider their network requirements and carefully compare these to SSE vendor offerings. This is due to different vendors offering different key features and therefore not all vendors will suit every business’ needs. It is important for IT decision makers to consider factors such as the breadth of security capability required, their legacy systems and how they may integrate with SSE, requirements for network scalability and SSE vendor reputations within the market. By considering these factors, IT decision makers can make the most well-informed choice to provide the best SSE solution for their network.
Furthermore, once integration has been started, continued attention should be given to several elements. This includes ensuring that legacy systems are correctly integrated, IT staff are retrained to use the new systems and security policies are adapted to account for the network leveraging the cloud. By doing so, organisations minimise the potential for creating weaknesses within the system and therefore improve the security of the network.
Future Outlook
In the future, further innovations using artificial intelligence to improve security are expected. This includes improvements to data analysis, autonomous response mechanisms, faster threat detection and proactive security measures which should minimise the need for manual monitoring or input from network administrators, therefore improving security response times whilst reducing workload for network administrators.
As regulations change, such as amendments to data privacy laws, this may cause adaptations to SSE solutions in order to fulfil these requirements. As SSE is a cloud-delivered service, this means that unlike with traditional networks, organisations will not need to purchase new hardware appliances to become compliant with changing regulations.
As Gartner has developed a magic quadrant for the SSE market, it shows that the segment is growing and therefore is an important component on its own for managing a network. This emphasises the impact that SSE is having on network management for organisations and its importance going forwards.
Conclusion
There has been a significant shift in the approach towards network security, with Security Service Edge enabling the increased utilisation of the cloud and remote workforces.
SSE provides an important role within the SASE framework, focusing entirely on the security of networks and ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of the network, whilst SASE implements SD-WAN performance benefits to ensure availability of the network. The introduction of artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques to SSE has enabled proactive threat detection, whilst cloud-delivered intelligence backed up by large datasets enables zero-day threats to be mitigated rapidly. Whilst IT decision makers must become aware of the challenges and considerations for implementation, the benefits that SSE provides to the network improves the overall network security, compliance with regulation and reduces both network administrator workload and the overall cost of the network infrastructure.