What is Zero Touch Provisioning
| Zero Touch Provisioning allows for automatic deployment of new network edges through remotely sent SD-WAN edge devices. |
One of the greatest challenges for global enterprises has been the setup and deployment of new network edges that are dispersed across a wide range of geographical locations, whilst minimising costs of deployment. Traditionally, this would have required experts to either travel with, or localised experts employed at the deployment site in order to get the network up and running. Businesses have noted that removing the costs of both local and travelling expertise can be achieved through automated deployment processes.
Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP) enables businesses to automatically configure and deploy their new network edge devices, such as within Software Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) solutions. Deploying with ZTP means that businesses can rapidly setup new network edges that maintain consistency with the rest of the network. This benefit makes ZTP ideal for minimising occurrences of human error within setup processes.
How Zero Touch Provisioning Works
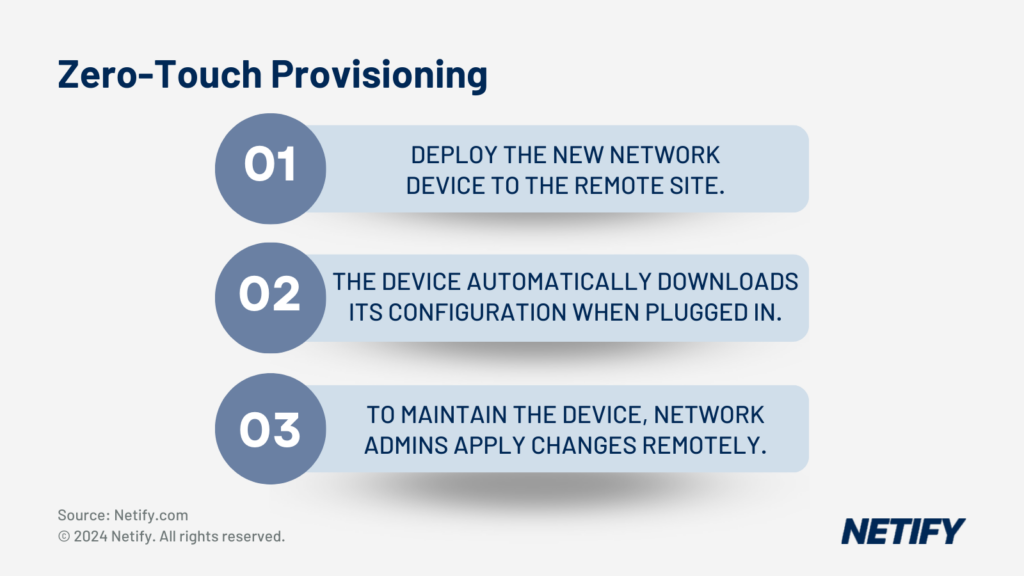
Zero Touch Provisioning takes new network edge devices through a set of instructions as soon as they are connected to the internet. This instruction set includes:
- Network discovery.
- Locating the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
- Enabling ZTP Server Discovery.
- Sends the device ID and connects to the pre-configured ZTP server (typically at a DNS address such as ztp.SD-WAN_Provider.com).
- Once configured and deployed, the device will be authorised with the ZTP server, with network parameters and security policies applied.
- Any final firmware updates and custom scripts are then executed to finalise the edge setup.
Key Applications of Zero Touch Provisioning
The most common use case for Zero Touch Provisioning is within SD-WAN. ZTP enables businesses to quickly deploy new edge devices so that the network can be expanded across new locations. The benefit of ZTP for SD-WAN is that it can use a single configuration as a template, ensuring that different branch offices conform to consistent policies, regardless of the connectivity types, such as MPLS, broadband and 5G.
For businesses that use more traditional network setups, often a centralised data centre is imperative to daily operations. ZTP enables enterprise data centres to rapidly scale its servers and equipment by ensuring that they are all deployed to a set standard.
However, enterprise data centres aren’t the only large-scale system to utilise ZTP, with cloud infrastructure also making use of ZTP capabilities in order to create their Virtual Machines (VMs) and offer their cloud services.
Alternatively, when considering the much smaller scale, Internet of Things (IoT) devices also use Zero Touch Provisioning. Typically, these devices lack any onboard security and so to efficiently integrate these devices into existing networks with security features, ZTP is leveraged.
Benefits of Zero Touch Provisioning
The benefits of ZTP primarily come from the reduction in human-led activities. Automatic processes increase efficiency and reduce the time needed to deploy new edge devices.
By ensuring consistency between edges, organisations can be re-assured that their network meets regulatory compliance requirements, as well as maintaining overall security.
Challenges and Security Considerations
Although there are many benefits to utilising Zero Touch Provisioning, it is also important to consider the potential challenges it may introduce.
One of these challenges is the initial configuration with the ZTP server and definitions of policies. This often requires expertise in order to achieve and therefore, whilst ZTP reduces the complexity of network administrator workloads, it should be noted that some expertise may be required for the initial design of the ZTP implementation.
There are also physical security risks that should be considered. By deploying networks remotely, businesses should consider the security of the devices against unauthorised access or tampering, as this can lead to both a local and entire network breach.
Finally, the variability between vendors is significant and therefore not all ZTP implementations are built equally, are as easy to implement or offer the same range of features.
Emerging Trends and Future Directions
The introduction of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into networking solutions does alleviate some of the challenges faced by businesses, with regards to complexity of deployment processes. The simplification of network processes is reflected within ZTP as AI enables adaptation of network configurations to suit available paths and ongoing network conditions. This reduces the complexity of deploying SD-WAN and removes the need for expertise when doing so, allowing for even novice administrators to deploy a network edge.
As well as AI, Edge computing has also become more prominent, allowing for integrations such as Internet of Things (IoT) to be implemented within business networks. Edge computing reduces the volume of traffic being transmitted across the network by ensuring that the majority of data processing happens at the network edge, rather than having raw data passed from edges to centralised processing centres. With edge computing becoming more viable, combined with the roll out of 5G mobile networks providing speeds comparable to broadband, businesses can now utilise ZTP with 5G to setup new IoT network edges for complete automation of processes.
Arguably the most important trend is that vendors are beginning to standardise ZTP operations, which allow businesses to utilise multi-cloud and hybrid environments with a single ZTP setup, rather than having to create multiple instances based on the cloud or environment due to be deployed.
Conclusion
Zero Touch Provisioning is primarily used to simplify the deployment across a multitude of use cases. By automating deployment processes, businesses can save time, cut costs and minimise the risk of human error being introduced into the network. Given its wide range of applications, ZTP is a core feature in SD-WAN, data centres and Internet of Things integrations.
Whilst the initial setup of ZTP configuration can often be complex and vendor differences only emphasise this, the introduction of artificial intelligence allows for assisted ZTP setup and standardisation has reduced the differences in ZTP, simplifying implementation.
This means that ZTP has become an essential feature for businesses with rapidly growing networks.