| SD-WAN can support MPLS but is increasingly preferred with public internet connections, offering better cost and flexibility for modern cloud-based needs. |
SD-WAN technology can support MPLS as one of several types of connectivity. It is designed to be connectivity agnostic, meaning that service providers can offer support for MPLS, as well as internet service provider connectivity across 4G, 5G, and Ethernet leased line technology. However, it is not necessary to use MPLS in order to operate SD-WAN. In fact, many enterprise businesses prefer to use public internet access instead of MPLS to improve the security of their devices, users, and public cloud access.
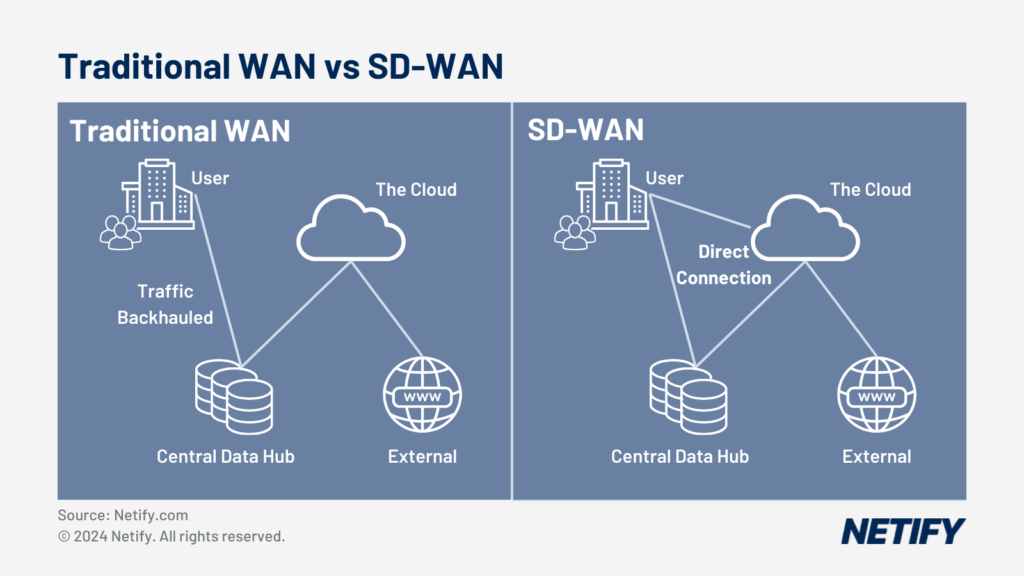
Traditional WAN vs SD-WAN - Traditional WAN vs SD-WAN
SD WAN use with MPLS
SD WAN use with MPLS is often implemented within an enterprise’s hybrid WAN architecture as follows:
- Where a business requires private layer 3 or layer 2 connectivity between selected sites or data centre locations
- Where specific latency and jitter requirements are needed between two or more locations
- Where the business remains in a contract at specific sites
- Access to private cloud infrastructure from branch-office sites
In summary, many IT decision-makers now prefer to use SD WAN technology with internet connectivity, resulting in a decline in the usage of traditional MPLS services. However, while SD WAN can operate across the public internet, SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) and SSE (Security Service Edge) are perceived to offer greater security compared to standard MPLS services.
SASE and SSE
SASE and SSE are essential in enabling remote users and branch offices to access cloud-based applications from any device, and can be used in conjunction with MPLS. However, it is important to note that the privacy provided by MPLS means that a public breakout is necessary to access internet-based applications.
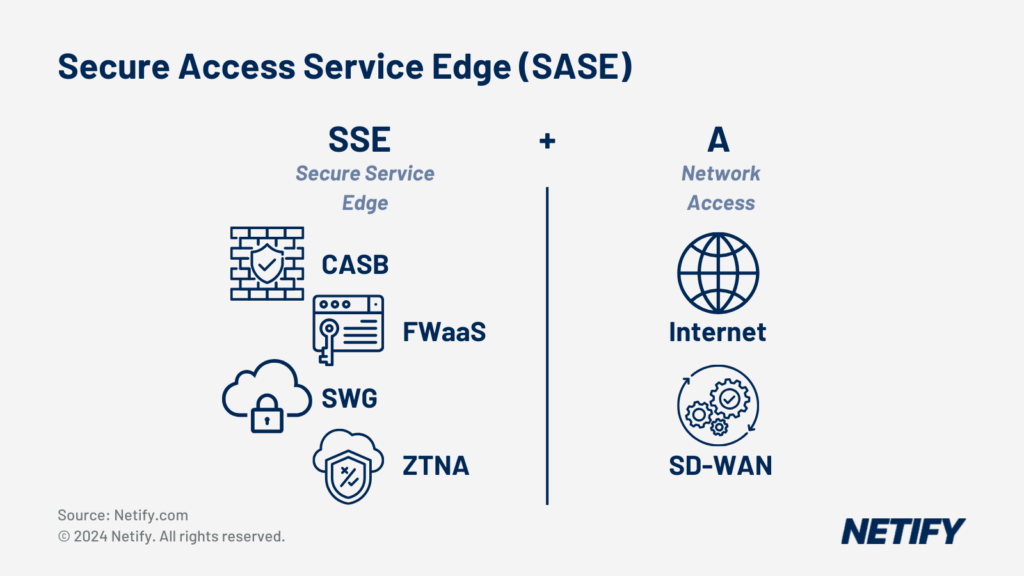
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) is SSE + SD-WAN (Access). - Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) is SSE + SD-WAN (Access).
Conclusion
Nowadays, deploying SD WAN instead of MPLS only makes sense in specific use cases, as most enterprise businesses find that Software WAN services offer better cost and features. In other words, since most users require 24/7 internet access, MPLS is no longer a suitable technology.


