| SD-WAN for healthcare enables secure, reliable and scalable connectivity for patient care and telehealth support. |
Attacks aimed at healthcare organisations have proven very costly for those affected, with some attacks causing tangible impact to patient care. While many healthcare organisations may feel as though they are overburdened with regulation, plenty of security practitioners argue that there aren’t enough.
Choosing the correct infrastructure to provide high-quality patient care, ensure the protection of network resources and improve operational efficiencies sounds daunting, however in this article we look into how Software Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) solutions can offer the networking architecture you need to address these issues.
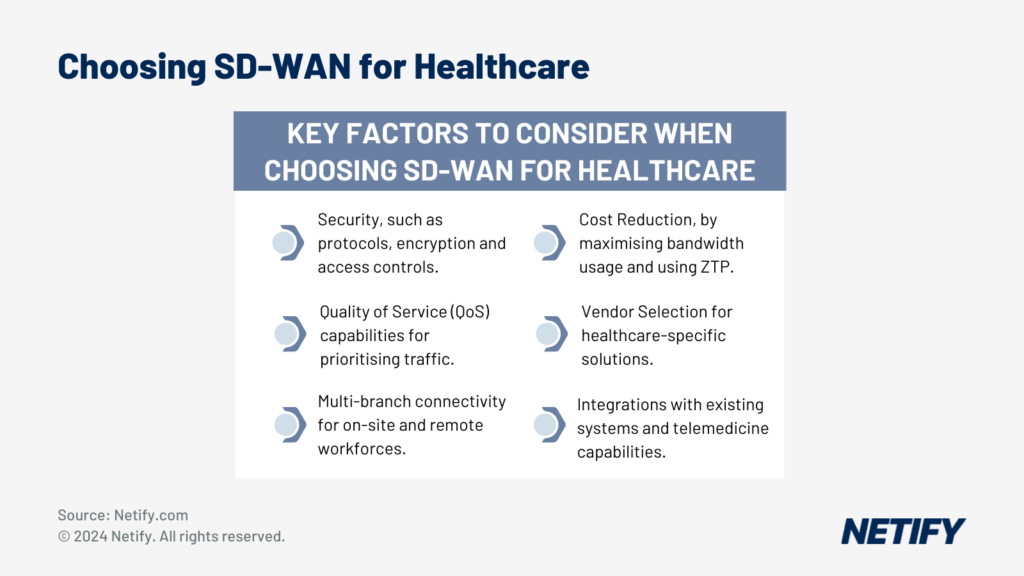
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing SD-WAN For The Healthcare Sector
Table of Contents
Healthcare-Specific Network Requirements
The healthcare sector requires constant availability for data, with continuous access to systems for emergency response, patient monitoring devices and electronic health record (EHR) systems to name a few. Traditional networks can be lacking in this feature, with network outages causing delays or even disruptions to systems, which can be a threat to patients experiences and health. This is however mitigated by SD-WAN, which offers the capability to leverage multiple network links, providing advanced failover functionality. Failover minimises network downtime, ensuring critical systems receive an uninterrupted connection via dynamic path selection techniques. These techniques utilise the best performing link based on real-time network metrics, reducing latency and transmission of data over disrupted links.
Not only is the availability of systems critical to healthcare, but so are the confidentiality and integrity of patient data. Regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), which mandates that healthcare provides must protect and correctly handle sensitive patient data. SD-WAN comes with integrated features to meet these needs, such as end-to-end encryption, secure tunnelling and compliance reporting, all of which help maintain the confidentiality of patient data and all regulations are complied with.
Another consideration for healthcare organisations is that they must also consider the scalability and flexibility of their network solutions. As patient data continues to grow rapidly, the network must be able to handle increased data loads without any compromise to performance. SD-WAN solutions offer the scalability needed to adapt to these changes, providing seamless connectivity across various sites and accommodating future growth in data volume and complexity.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing SD-WAN for Healthcare
Healthcare networks have become a prime target for cyber attacks, something Synnovis (a private pathology firm that processes blood tests for major London NHS hospitals), the victim of an attack in June 2024 can attest to. Threats created by malicious actors seek patient data, enabling hackers to hold victims to ransom or allowing the information to be sold on dark web marketplaces. This emphasises the importance of securing the network, utilising advanced security protocols, strong encryption and secure access controls – features all provided by SD-WAN solutions.
Unlike traditional WAN networks, SD-WAN provides Quality of Service (QoS) management, functionality to create policies defining critical traffic that requires the most reliable performance. For healthcare providers, QoS enables the ability to prioritise bandwidth-intensive applications, such as telemedicine, radiology imaging and real-time video consultancy, ensuring adequate network resources are provided to these systems in order to prevent any degradation of traffic.
For providers split across multiple sites, such as hospitals, clinics and mobile or remote workforces, it can be very difficult to create network access across these different network edges. However, SD-WAN is geared for multi-branch connectivity, enabling both on-site and remote workforces and providing rapid scalability for new sites and increased data loads.
Not only does SD-WAN offer network improvements, but it can also offer a reduction in operational costs. By being more resourceful about bandwidth usage in comparison to traditional WAN networks, healthcare providers do not have to run dedicated lines between machines. SD-WAN’s managed through a single pane enables remote configuration and management, and when bundled with Zero Touch Provisioning, it enabled scaling to new sites without on-site specialised network administrators. Through reductions in specialised staff, healthcare providers can save costs with a single dedicated team to manage all sites remotely.
When choosing security products, services and vendors, it may seem like every manufacturer and vendor has something specifically geared toward the healthcare industry. While some companies have more healthcare experience than others, the availability of solutions catered to the industry is a great thing thing because healthcare organisations have to worry about the entire range of cybersecurity threats including some of the most prevalent from ransomware, to IoT security, application security and vendor risk management. So, while there’s no shortage of commercial solutions for every aspect of a healthcare organisation’s cybersecurity needs, it is vital that the organisation adopts a robust cybersecurity framework to align business and regulatory needs with solutions to stay secure and remain compliant.
Supporting Telehealth and Remote Patient Care
SD-WAN supports Telehealth functionalities such as remote consultations by enabling high quality video and audio connectivity, whilst also capable of creating secure connections for sharing patient data during Telehealth sessions. This gives healthcare providers the ability to not only provide real-time video consultations but improves patient access to healthcare services and enables healthcare professionals to deliver timely and accurate diagnoses, even in remote or underserved areas.
The reliability of connections is important for monitoring patients’ health metrics from home, such as with remote monitoring devices that track vital signs, glucose levels, or cardiac rhythms. SD-WAN provides secure transmission of data to centralised health systems, offering improved confidentiality and integrity for the network. This ensures that patient data remains secure while enabling healthcare providers to make informed decisions based on real-time data.
Integrating SD-WAN with Existing Healthcare IT Infrastructure
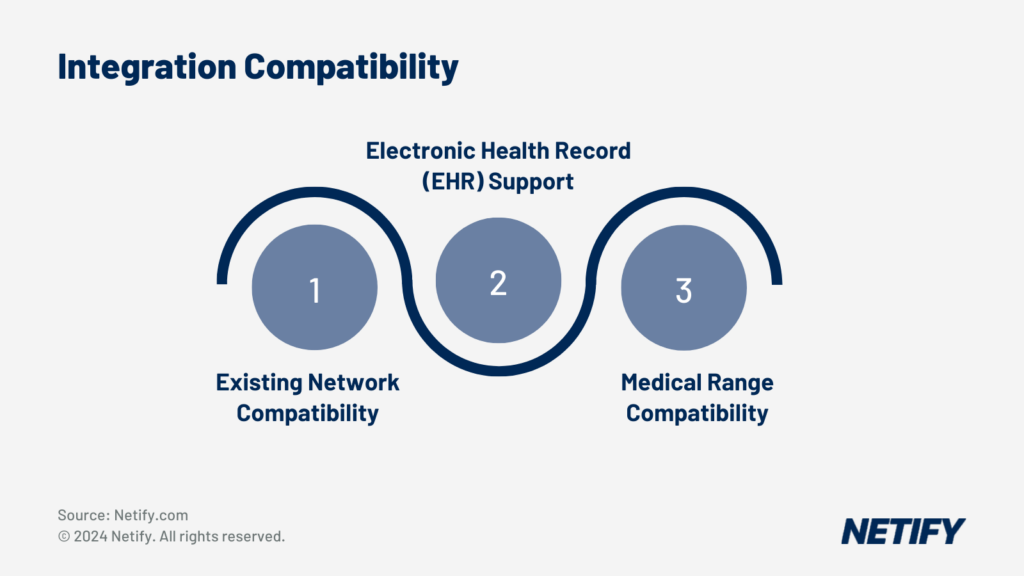
SD-WAN Healthcare Integration Compatibility
It is important for IT decision makers at Healthcare providers to select an SD-WAN solution that is not only feature-rich to meet demands, but is also compatible with existing healthcare infrastructure. A seamless integration of SD-WAN with the existing Electronic Health Record (EHR) is essential to minimise potential disruptions during the migration process. This integration ensures that healthcare providers can maintain continuity of care and access to patient records without interruption.
Any chosen SD-WAN solution must also support connectivity for a wide range of medical equipment, in order for real-time communications from devices such as MRI machines, infusion pumps and patient monitoring systems. Compatibility with these devices ensures that healthcare providers can leverage the full potential of their medical equipment while maintaining secure and reliable network connections
Future-Proofing Healthcare Networks with SD-WAN
As healthcare embraces IoT devices for patient monitoring and smart hospital systems, as well as Artificial Intelligence (AI) driven diagnostics and personalised medicine, the SD-WAN solution should be capable of supporting these advancements. The integration of IoT devices in healthcare can lead to improved patient outcomes, operational efficiencies, and cost savings. Therefore, it is essential that the SD-WAN infrastructure can handle the increased data traffic and provide secure connectivity for these devices.
Finally, the scalability of SD-WAN to meet future increases in the volume of data handling is an essential feature, enabling support for new healthcare applications and innovative healthcare delivery models such as home healthcare and mobile health units to be supported. This scalability ensures that healthcare organisations can continue to innovate and expand their services without being constrained by their network infrastructure.
Conclusion
As networks are becoming ever-more crucial to healthcare providers, both for general operations and for regulatory compliance, it is difficult for the IT decision makers at healthcare providers to find a solution to fit all problems. With a need to enhance security, support telehealth services, integrate with existing network infrastructure and future-proof their networks, the best choice has to be SD-WAN, which offers resolutions for each of these issues.


