| SD-WAN enhances remote work by improving connectivity, security, and performance. It leverages multiple network links, integrates advanced security, and offers centralised management to ensure uninterrupted and secure access for remote workers. |
As remote working practices are increasingly being adopted by businesses, it has highlighted the importance for businesses to provide reliable and secure connectivity to both home and remote locations to ensure productivity is maximised. Traditional WAN architectures have often struggled with this, leading to complex integrations and poor application performance for users. These issues have been addressed by Software Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) solutions and in this article, we investigate how SD-WAN can enhance connectivity, security and efficiency for remote workforces.
- SD-WAN For Remote Workers
Enhanced Connectivity for Remote Workers
Broadband and LTE/5G Integration
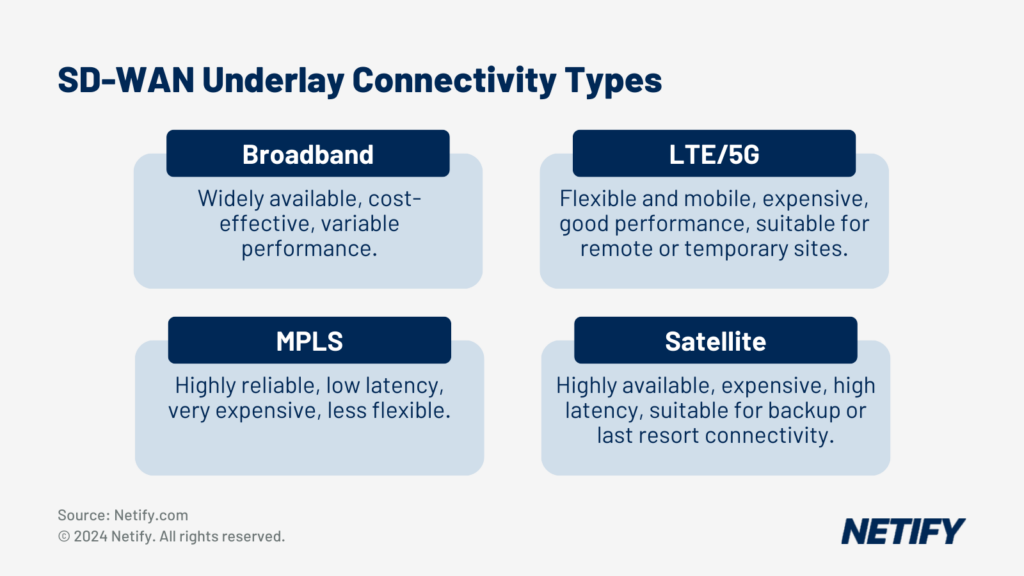
- The 4 main underlay types for SD-WAN.
One of the key benefits of SD-WAN solutions is the ability to leverage multiple internet connections, such as MPLS, broadband and LTE/5G. Leveraging multiple communication types is essential for remote workers, with both broadband and LTE/5G coverage ensuring that users get uninterrupted access to corporate resources, even if one connection fails.
This functionality is extended by the ability for SD-WAN to utilise Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP), enabling the rapid deployment of new devices through devices being deployed to site and remotely or automatically configured.
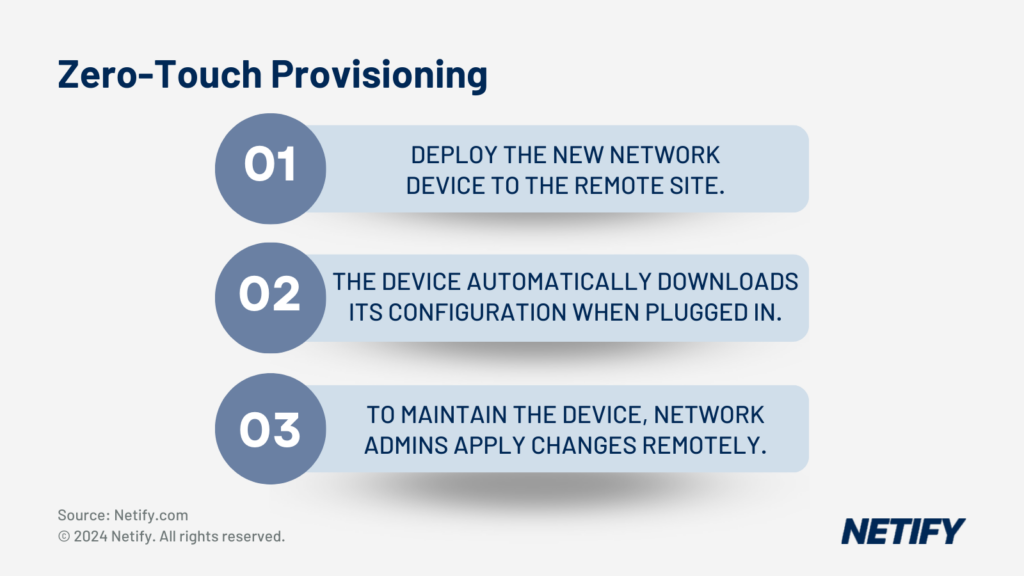
- The steps of Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP)
By using ZTP with remote workforces, businesses can simplify home-office network setups through automated configuration, which reduces the complexity and burden on both the home-user and potential network engineers that would otherwise need to visit the home.
Bandwidth Optimisation
Whilst leveraging multiple network links ensures uninterrupted connections, SD-WAN can also optimise bandwidth utilisation. This process involves intelligently routing traffic across each communication link based on application requirements and network conditions. Network telemetry details the health of each link, its current performance and, to ensure critical applications receive necessary bandwidth, SD-WAN routes traffic over the most appropriate link, improving overall performance and user experience (UX).
Security Measures for Remote Access
Integrated Security Features
SD-WAN integrates various security features to ensure the protection of remote workers, which include features such as firewalls and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) to prevent security breaches. This is essential for protecting remote connections, where it is inappropriate to install dedicated machines to handle all of these functions, which would typically have to be done for traditional WAN networks. This added layer of security for remote workers ensures data confidentiality and integrity by preventing breaches, meanwhile ensuring availability by preventing downtime from potential breaches.
By offering these security features through a single pane as part of the SD-WAN solution, it reduces the need for complex architecture, minimises the amount of configuration for network administrators and reduces the overall attack surface for threats.
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
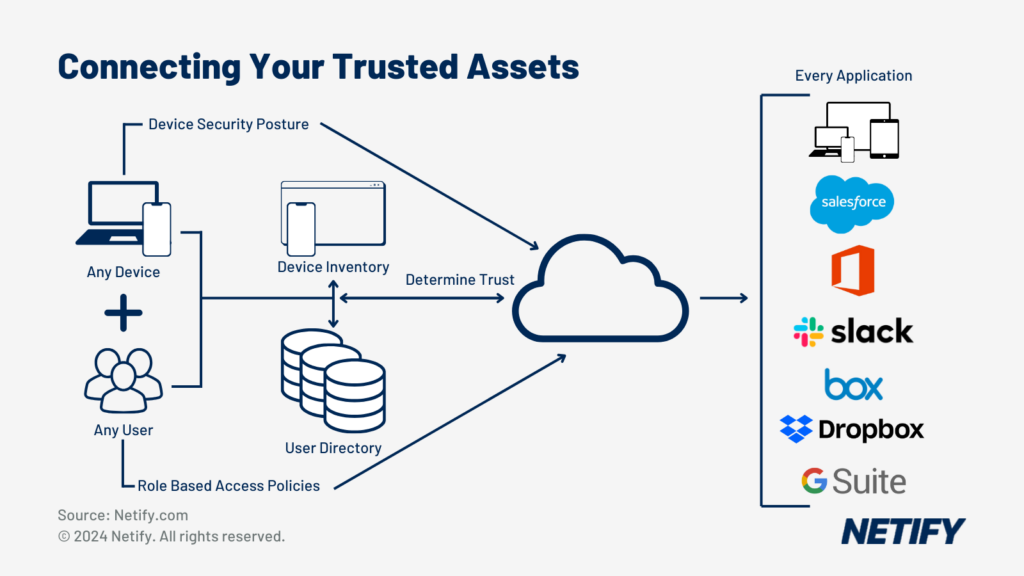
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) within SASE
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is a security principle that defines that networks should “never trust, always verify”. With ZTNA, the network assumes that no device, user, or physical connection should be inherently trusted by the network and so these all require constant authentication to initially gain but also to maintain access to the network at every interaction. By enforcing these granular access controls based on user identity, device posture and application requirements, SD-WAN leverages ZTNA to ensure only authorised users and devices can gain access to specified resources, which is essential for remote connections.
One example of why this is important for remote workers is protecting against threats when using public Wi-Fi connections. When connected to public Wi-Fi, bad actors can utilise techniques such as Session Hijacking, enabling malicious activities such as stealing identify information or session tokens, which may compromise business networks. By applying ZTNA to this scenario, the constant re-authentication of both user and device ensures that a session has not been hijacked and helps protect the integrity and confidentiality of the network.
Application Performance and Reliability
Application-Aware Routing
One way that SD-WAN improves application performance and reliability is through its application-aware routing capabilities. Application-aware routing allows network administrators to define prioritisations for traffic directly within the SD-WAN controller based on the specific requirements of the application. This means that latency-sensitive applications such as VoIP and video conferencing are routed via the lowest latency path, whilst bandwidth-intensive applications are routed across paths with high bandwidth availability. This is important within remote settings as network links may be limited and therefore prioritising the routing of essential applications over the strongest links can have a huge impact for performance and user experience.
Failover and Redundancy
By leveraging multiple network links, SD-WAN also provides automatic failover mechanisms in the event of a single link going down. By seamlessly switching traffic to a secondary connection on failure of the primary link, this ensures uninterrupted access to the network, preventing downtime and maintaining productivity for remote workers.

- Application Performance and Reliability Benefits
Simplified Management and Deployment
Centralised Management
In order to simplify the management of network processes, SD-WAN offers a single centralised pane, enabling remote deployment, configuration and monitoring capabilities. This enables network administrators to configure, monitor, troubleshoot all remote worker’s networks from a single platform, reducing operational overhead and improving visibility of all network activities.
Policy-Based Control
When configuring the network, administrators will typically implement the policy-based control features offered by SD-WAN. By defining application-specific rules, security policies and Quality of Service (QoS) parameters, these configurations can be automatically deployed to remote sites, ensuring consistent enforcement of policies within the network, regardless of location. This is essential for businesses to meet requirements such as regulatory compliance, with these policies being used to segment traffic from different applications, which is critical for businesses that need logical separation of industrial systems from enterprise networks, mandated by ISA/IEC62443.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Examples of Successful Implementations
Many companies have successfully implemented SD-WAN to support their remote workforce. One example of these is a global financial services firm, which deployed SD-WAN to provide secure and reliable connectivity to its employees working from home. The SD-WAN solution enabled their remote workforce to utilise seamless access to critical applications, ensured all workers experienced an improved network performance (when compared to traditional WAN) and given the nature of the business, strict and enhanced security measures to protect data both in-transit and at worker’s homes.
Lessons Learned
Learning from other’s mistakes can be a great way for businesses to minimise financial wastage and this is also true when considering implementing an SD-WAN solution for your workforce. Businesses that have failed in their implementations have often forgotten some key considerations when moving to SD-WAN, such as the need for thorough network planning, employee training, ongoing monitoring and optimisation, whilst also determining the level of scalability and flexibility required to meet future business needs. By addressing these issues proactively, businesses can avoid common pitfalls and ensure a smooth transition to SD-WAN, enabling the full benefit of these features to be experienced.
Future Trends and Developments
- Future Proofing With SD-WAN
Advancements in SD-WAN Technology
As Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning integrations within SD-WAN become more prevalent, it is important to understand the different use cases for each across different SD-WAN vendors.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have been integrated to produce tools that assist with the predictive maintenance and anomaly detection of SD-WAN networks. These technologies monitor network traffic, finding patterns within said traffic. These are then able to match these patterns up against expected behaviours (from users) or potential threats to the network and thus enables a proactive approach to dealing with these potential threats.
Additionally, AI and ML are being used to automate networks through the process of managing traffic routing and security policy updates. This reduces the workload on network administrators and simplifies the management of the network.
Impact of 5G
The rollout of 5G has also had a significant impact for SD-WAN solutions, with 5G providing a significant performance improvement over 4G (up to 10 times faster), making the use of cellular data services a more viable option for remote worker connectivity. Through high bandwidth and low latency offerings, 5G has not only improved performance but has also increased reliability, which in turn assists in improving the overall user experience.
Conclusion
SD-WAN offers significant improvements for connectivity options, reliability, security and performance over traditional WAN networks for remote workers. By leveraging multiple network connections, optimising bandwidth usage, integrating advanced security measures and simplifying network management, SD-WAN offers businesses with an easy solution to manage their remote network efficiently, improve productivity and ensure the confidential and integrity of the network when using a remote workforce.


