| SD-WAN outperforms traditional WAN by offering cost efficiency, flexibility, enhanced security, and dynamic performance, making it ideal for cloud-first, scalable networks. |
In recent years, the widespread adoption of cloud computing, remote workforces and increased network demands has required organisations to seek more agile, cost-effective solutions that can meet their performance, security and reliability requirements. Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) solutions have emerged as the best alternative to traditional WAN networks, by addressing the flexibility, security and performance limitations that traditional networks experience.
In this article we explore the key differences between SD-WAN solutions and traditional networks and the benefits that SD-WAN has to offer your business network.
Table of Contents
The Evolution of WAN Technologies
When considering how SD-WAN can improve your business network, it’s important to understand the reason for its emergence.
Understanding Traditional WAN
Traditional WAN networks typically utilise Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) or leased lines in order to provide network connectivity. Whilst MPLS is well renowned for its guaranteed speeds and Service-Level Agreements (SLAs), it also comes with high costs and the rigidity that comes with using only a single network link, which limits scalability and makes larger networks more complex to develop and manage. The complexity of management processes is only highlighted by traditional WAN networks limited visibility into applications and performance, whilst also providing limited control of network traffic.
The Rise of SD-WAN
Businesses are increasingly leveraging the cloud for Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) in order to take a cloud-first approach. This increased reliance on cloud services has highlighted the inefficiencies of traditional WAN, with MPLS links not optimised for localised breakouts to the cloud. SD-WAN resolves this issue, whilst also adding flexibility to the network for mobile and remote workforces by enabling businesses to leverage multiple transport links. Combining broadband, LTE and MPLS, SD-WAN is capable of optimising traffic performance, increasing cost efficiencies, improving agility and scalability and reduces organisations dependency on MPLS links in a predominantly cloud-using infrastructure.
Cost Efficiency and Flexibility
The difference in cost efficiency isn’t solely limited to the cost of network links, SD-WAN can in fact improve business cost efficiencies in other ways.
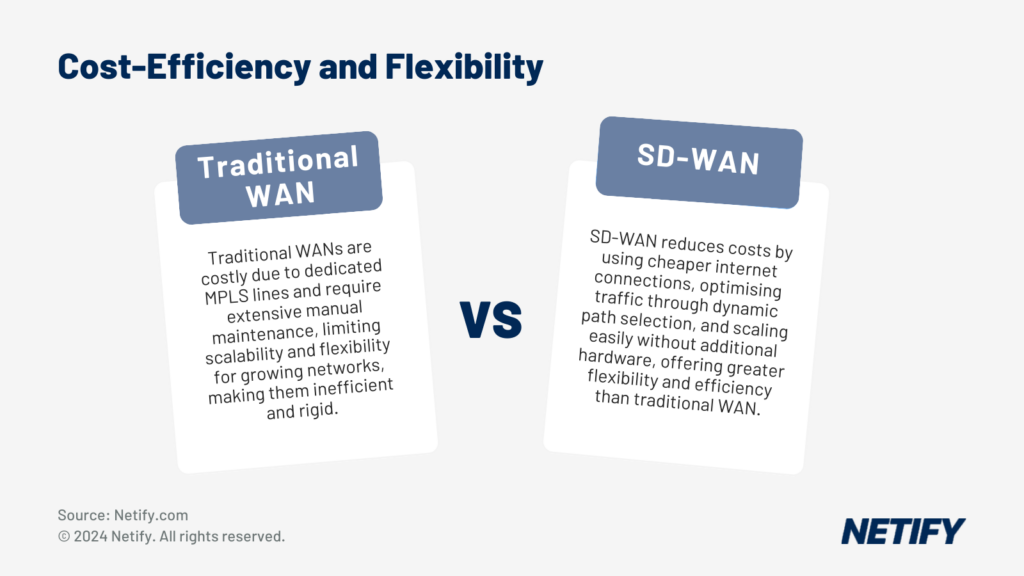
Cost-efficiency and flexibility in traditional WAN vs SD-WAN - Cost-efficiency and flexibility in traditional WAN vs SD-WAN.
Traditional WAN Costs and Constraints
Traditional WAN does typically have a higher cost, given MPLS acts as a dedicated line designed for maximising performance, this is reflected in its pricing. But this isn’t the only constraint, with network administrators having to do lots of manual maintenance to retain consistent reliability and performance in a changing environment. This rigidity of the network and its configurations limits the scalability and reduces the flexibility for organisations with a growing network.
The SD-WAN Advantage
Although SD-WAN can utilise MPLS network links, SD-WAN can also leverage multiple cheaper internet connections for a reduction in overall network cost. By using a range of links, SD-WAN can apply dynamic path selection and Application Aware Routing (AAR) to transmit application traffic, load balancing the network and preventing the need for additional links to be deployed, reducing costs.
Further to this, the software-based nature of SD-WAN allows for greater scalability, simplifying the complexity of upgrades and reducing the need for additional appliances or hardware to provide new functionality, therefore saving organisations from exorbitant hardware costs and maximising the efficiency of the hardware being utilised.
Enhancing Network Performance and Path Selection
The differences in network architecture can have a massive impact on performance and how application traffic is prioritised.
Challenges with Traditional WAN
Traditional WAN uses static path routing, with routing configurations manually set by network administrators, not allowing for adaptability should network demands and requirements vary frequently. This inadaptability introduces inefficiencies into the network and can also cause suboptimal cloud-based application performance.
Innovations in SD-WAN
SD-WAN mitigates the issues with traditional WAN by providing dynamic path selection and Application Aware Routing with routing decisions based on real-time network telemetry data. This ensures that traffic is sent over the best possible path to reduce latency and adhere to Quality of Service (QoS) configurations for prioritisation of critical operations.
For optimising cloud-based application performance, SD-WAN enables cloud connections via on-ramping capabilities, creating a direct connection from branch offices to the cloud, reducing the need to backhaul data to a central data centre, as is used in traditional WAN solutions that make use of MPLS. Due to the ability to create direct connections from users to the cloud, SD-WAN is therefore especially applicable in organisations utilising Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS).
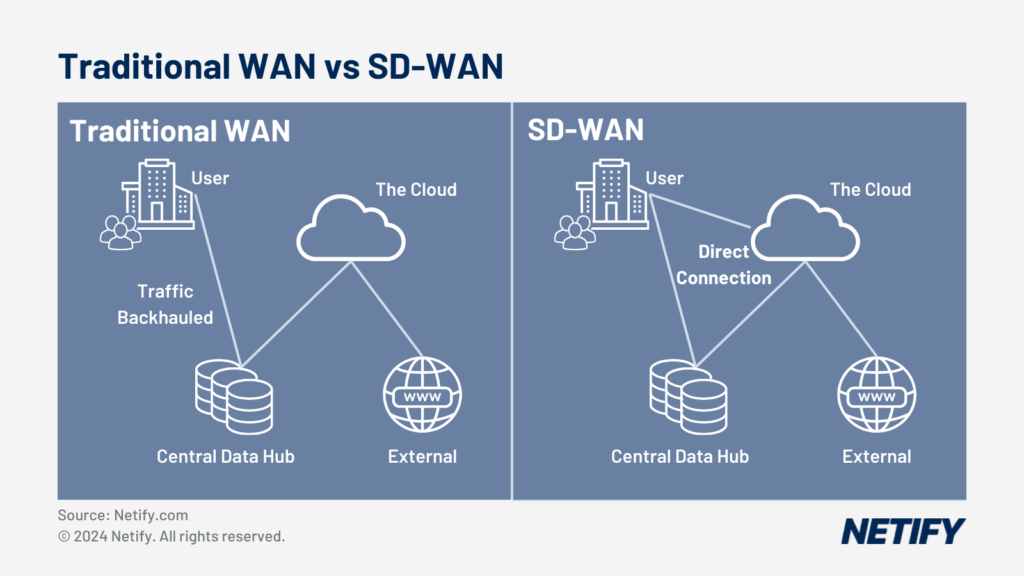
Traditional WAN vs SD-WAN - Traditional WAN vs SD-WAN
Enhanced Security with SD-WAN
The improvement to the network is not limited to performance increases though, with security functionalities also being improved by SD-WAN.
Security Limitations of Traditional WAN
Traditional WAN manages its security over a range of appliances, which comes with added cost per appliance/hardware component and, with a larger number of appliances, introduces complexity for integrating and managing all security systems, which in turn can result in potential vulnerabilities due to incompatibility or misconfiguration due to complexity.
The Security Convergence in SD-WAN
Unlike traditional WAN, SD-WAN offers built-in security functionality, such as Next Generation Firewall (NGFW), Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and advanced threat protection for streamlined security processes.
The emergence of Secure Access Service Edge (SASE), converging SD-WAN and Secure Service Edge (SSE), which integrates security services like Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and Secure Web Gateway (SWG) into the network infrastructure. This unified approach for managing the SD-WAN network and the SASE security functionality ensures greater protection of the network by allowing network administrators to align their entire network and its processes with Zero Trust principles.
Support for Multiple Underlay Types
SD-WAN acts as an overlay network, allowing for support of multiple underlay types, which can be a benefit for businesses to improve their network efficiency.
Constraints of Traditional WAN
There are significant limitations to traditional WAN networks, which often depend on a single specific carrier network for their MPLS link. This results in vendor lock-in, limiting network flexibility and increases the reliance on the single type of underlay, which isn’t ideal in the event of link downtime. Further to this, this limitation also creates cost inefficiency and doesn’t allow for performance optimisations such as Quality of Service (QoS).
The Flexibility of SD-WAN
By comparison, SD-WAN offers vastly more flexibility than traditional WAN, enabling businesses to utilise various underlay link types, such as broadband, LTE, MPLS and satellite. Organisations can therefore improve their network through cost efficiencies, performance optimisations and supporting better-compatible underlay links for specific requirements or distributed systems. This means that network infrastructure can be tailored to suit a diverse range of use cases and geographical considerations, whilst maintaining reliability, performance and connectivity.
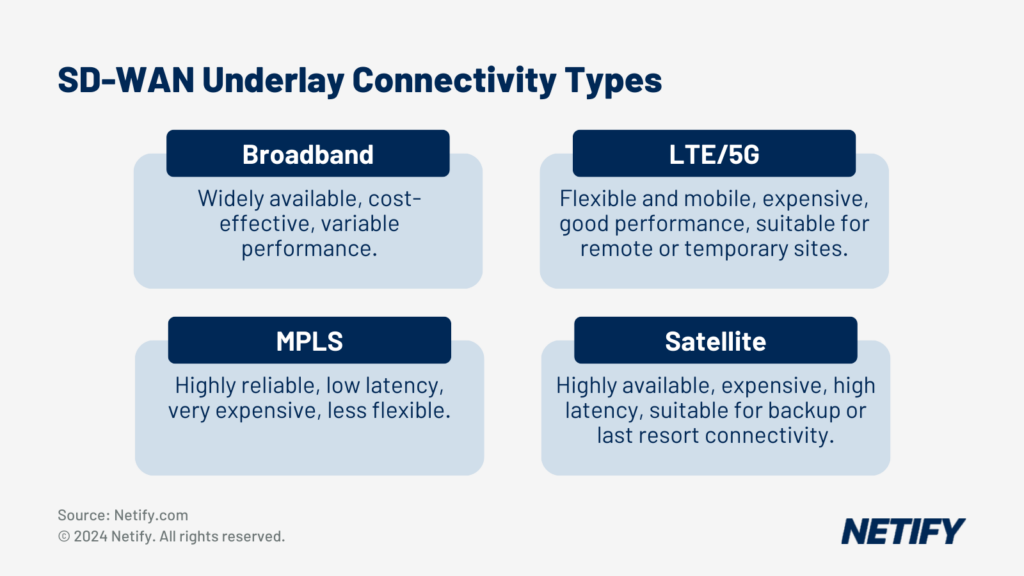
SD-WAN Underlay Connectivity Types - The 4 main underlay types for SD-WAN.
Simplified Management, Reporting, and Statistics
The management styles for each architecture are vastly different, with traditional WAN requiring a lot more management for less-optimised performance.
Traditional WAN Management Challenges
Traditional WAN management requires continuous manual monitoring and troubleshooting to maintain optimal performance. This makes it difficult to improve performance and quickly resolve issues.
SD-WAN’s Centralised Management Benefits
SD-WAN improves upon traditional WAN by providing network administrators with a single interface with the capability for automation, coordination of network functions, and policy enforcement across the entire network. This single pane for all network functionality simplifies network operations for network administrators and enables optimisation of application performance across the network whilst ensuring consistent security and compliance is followed by all users and devices.
This interface provides access to real-time network analytics, enhanced visibility of application performance and overall network health. Telemetry can be utilised by network administrators for proactive and efficient network management, allowing administrators to make informed decisions for optimising network operations, ensuring it can support the organisation strategy and objectives.
Managed Services and Future Trends
As more businesses shift to SD-WAN architectures, there have been many new trends within the sector.
Traditional WAN Service Models
Traditional WAN services have relied on in-house management teams or limited management from telecom providers, which can be restrictive, lack flexibility and does not support cloud-first models. This leads to inefficiencies in the network and increased operational costs, which in-house management teams may not be able to support.
The Shift to Managed SD-WAN Services
There has been a growing trend in businesses leveraging managed SD-WAN services. A managed SD-WAN service is provided by third parties, enabling businesses to outsource network management. Managed SD-WAN solutions encompass web-based reporting, automated traffic routing, and configuration, backed by SLAs, NOC monitoring, and support. Managed WAN services are designed to optimise network efficiency and reliability.
By expediting the deployment process, businesses can simplify the network management process and allows for ongoing optimisation, supporting demands for cloud-first network strategies.
The Future of SD-WAN
Future Proofing With SD-WAN - Future Proofing With SD-WAN
By integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into SD-WAN, it enables predictive analysis of network performance based on real-time metrics and historical data. This enables SD-WAN to optimise the network performance in real-time and respond to network issues proactively. Artificial Intelligence has also been integrated into SD-WAN in order to enhance security. These integrations detect threats (including Zero Day) and apply automated responses or notify network administrators before they can cause further damage to the network. These AI features are unique to SD-WAN when compared to MPLS as SD-WAN enables visibility into application behaviour, which was previously not possible with MPLS systems.
Further to this, SD-WAN is increasingly supporting a wider range of cloud services and edge computing. Edge computing has become a significant factor for network management when utilising manufacturing automation technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) and 4D vision.
Conclusion
SD-WAN represents a significant advancement over traditional WAN architectures, offering greater flexibility, cost efficiency, and enhanced security. As businesses increasingly adopt cloud-first strategies and remote workforces, the demand for an agile, and scalable network solution has never been more essential. SD-WAN not only addresses the limitations of traditional WAN but also provides a future-proof framework that supports the growing needs of organisations. By leveraging multiple transport links, centralised management, and integrated security features, SD-WAN enables organisations to optimise their network performance and reduce operational costs.


