The top 10 benefits of SD-WAN are:
|
Why IT Decision Makers Need to Understand SD-WAN Benefits
SD-WAN fundamentally changes the way an organisation’s network architecture is controlled, managed, optimised, and expanded. Unlike a traditional WAN setup using MPLS, SD-WAN enables businesses to harness dynamic routing capabilities, sending data over the optimal path based on real-time traffic and ensuring that crucial applications are always serviced.
The simplification of network architecture provided by SD-WAN assists network administrators with traffic control and policy management. The SD-WAN controller offers administrators an interface to control network policies that are universally applied across devices, reducing complexity and following the SASE framework. SD-WAN also includes enhanced security functionality and support for future technologies, removing the need for additional on-premises appliances and further simplifies the network architecture.
Another reason IT decision makers should understand the benefits of SD-WAN is that it is also essential for cloud architecture. This means that regardless of a public, private, multi-cloud, or hybrid cloud setup, SD-WAN facilitates secure and efficient connectivity for a more reliable network. Cloud integration with SD-WAN offers significant benefits, including cost savings, improved performance, and centralised control.
However, these aren’t the only benefits to SD-WAN:
Public Cloud Access
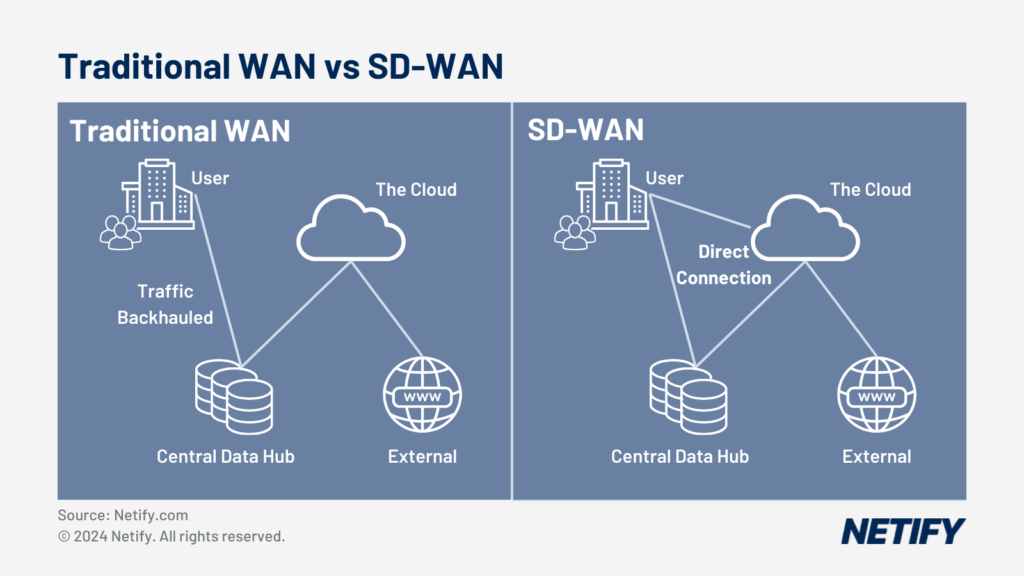
SD-WAN is instrumental in enabling a cloud architecture for a business. In traditional WAN architectures, traffic was backhauled via a central data centre before accessing the cloud, however due to SD-WAN, this is no longer necessary as SD-WAN can provide a direct connection to different public cloud services. This dedicated path means that direct connections between the network and cloud have higher bandwidth, with the network experiencing higher speeds, less latency and this provides an overall better performance for user experience (UX) encouraging greater productivity across the network.
This integration offers significant other benefits, including cost savings and centralised control. Businesses adopting this approach can leverage Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Logging as a Service (LaaS) more effectively across cloud platforms.
Leveraging Internet Services
SD-WAN improves the network performance by dynamically routing traffic via the best path based on real-time traffic analysis. This is further extended by the ability of SD-WAN to leverage multiple ISPs (broadband, 4G, 5G, LTE, internet leased lines and satellite services) and combine them to provide greater bandwidth for the network. This decreases the latency of the network and ensures reliability to crucial applications across the network.
As SD-WAN has the ability to route over many connections from different ISPs, this gives greater flexibility to IT decision makers as it increases accessibility by allowing lower cost links to be used whilst still maintaining crucial application performance.
Multi-Cloud Capabilities
SD-WAN enables seamless connections between multiple cloud platforms (such as AWS, Azure). This allows for redundancy and disaster recovery, reducing the risk of the network experiencing disruptions caused by outages by a single cloud provider as the additional cloud providers can be used as a failover system. This boosts the network availability and helps provide a good user experience.
Multi-cloud also allows for workload to be shifted between different cloud providers, balancing the overall load on any given cloud provider. This can be considered a benefit as multi-cloud may provide IT decision makers the ability to negotiate lower prices with cloud providers.
Integration with SASE
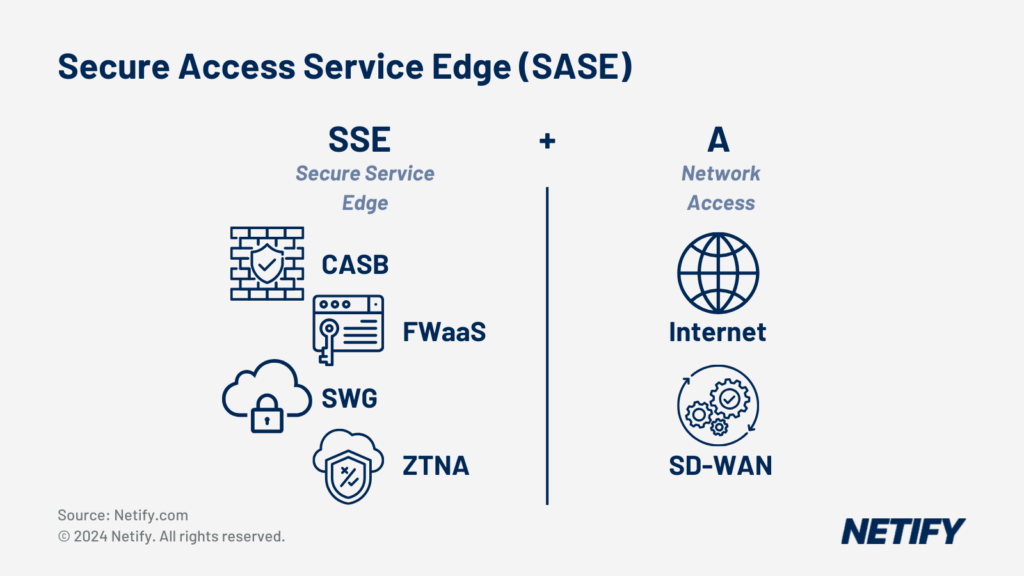
As SD-WAN moves the control plane to a centralised controller, this streamlines all processes. One of the processes that are streamlined is network security management. As also seen in the Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) framework, SD-WAN enables centralised policy enforcement and network-wide visibility of policies. For example, functions like Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS) can be managed via the central controller and applied across the entire SD-WAN infrastructure.
This means that SD-WAN aligns with the SASE framework as it enables IT decision makers to incorporate a more holistic, cloud-centric approach to network security by applying the same policies regardless of device or location. When integrated as a component of SASE, SD-WAN provides the scalable and flexible network architecture for delivery of cloud-based services. This is especially true within Internet of Things (IoT) environments, where large numbers of devices require streamlined policy enforcement.
As SD-WAN can function entirely within the cloud, the security services that SD-WAN contributes within the SASE model simplifies an organisation’s network and security architecture, enhances it’s security posture, scalability, and agility.
Traffic Prioritisation
SD-WAN improves on traditional WAN systems by enhancing traffic prioritisation. Traditional WAN uses MPLS which requires manual configuration of the static routing protocols and any failover/redundancy for each circuit. This does not allow for easy changes, as each MPLS will need manual configuration to amend the routing protocol.
Unlike MPLS, SD-WAN is able to dynamically route data. By considering real-time traffic, historical data and available network links, SD-WAN can prioritise crucial applications (via advanced Quality of Service policies) to ensure that these applications have higher bandwidths and the least-possible latency. This serves as a massive improvement on MPLS as the process is entirely automated and uses data to accurately route traffic at any given moment. By using these policies to prioritise crucial data flows, SD-WAN optimises the overall user experience (UX) by making the network more reliable for its user base.
Simplified Deployment
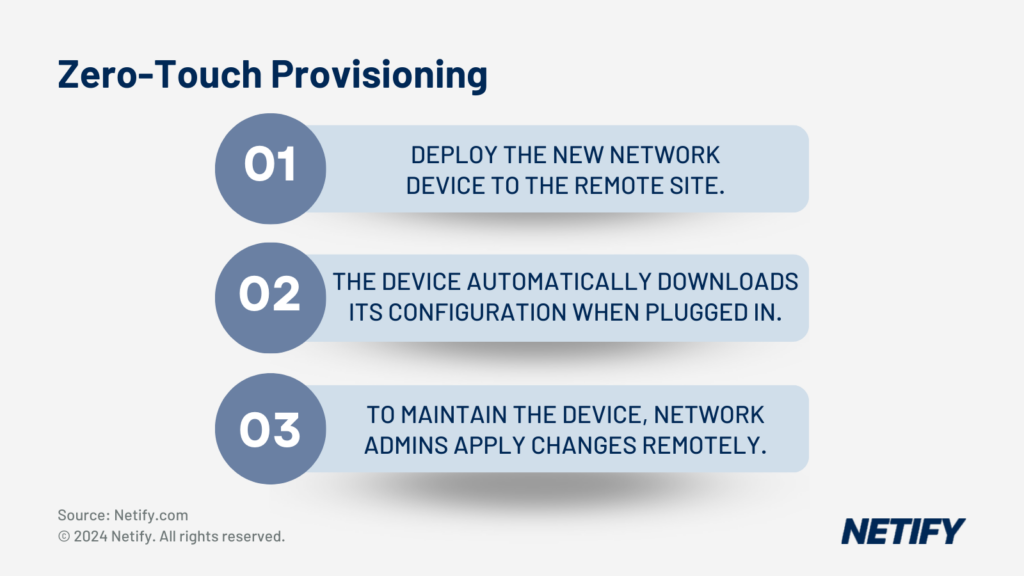
Via Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP), SD-WAN enables a simplified deployment model. SD-WAN is able to be deployed, controlled and configured remotely to provide the best configurations at any given moment, based on real-time network traffic.
When compared with traditional WAN systems, SD-WAN is also less complex. This is due to the control plane of a WAN being moved to a centralised controller within SD-WAN. This enables SD-WAN to offer automated configuration and deployment, which eliminates the potential for human error (as can often be seen on traditional WAN systems).
Previously, administrators would have to monitor link utilisation to manually configure routing policies in order to load balance the network. With SD-WAN, the load balancing process is entirely automated, simplifying the workload of the administrator and using real-time traffic data to exercise system agility and switch routing for traffic in order to better balance network load.
The Zero Touch Provisioning and centralised controller offered by SD-WAN give the network flexibility to adapt to evolving requirements, reduces the amount of manual configuration for administrators and allows for ease of scaling through remote deployment.
Enhanced Remote Access
Additionally to simplifying the deployment of SD-WAN, the centralised controller provides SD-WAN with easy access to policies changes and easy integration of new technologies. Due to being centralised, this enables connections to the controller remotely from any part of the network.
This remote access provides administrators with a single interface to interact with and reduces the workload of administrators as a single change on this interface will update the entire network with new policies and features. These are automatically pushed out and don’t require any additional configuration, reducing time taken to configure the network by administrators and ensures a consistent policy system across the network.
Enhanced remote access therefore provides businesses with not only a simpler system to manage but also increases the businesses agility through quicker changes to their network when compared with traditional WAN systems.
Network Optimisation
There are several ways in which SD-WAN optimises the overall network. To better optimise network communications, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are being used to consider historical data in order to carefully adjust the traffic routing strategy used by the network.
This ensures that the best route is decided entirely on automated data-driven analysis and with the help of AI predictive load balancing, IT decision makers can be sure that their network is capable of dynamically adapting to changing network requirements.
Additional, SD-WAN introduces security features for network optimisation. One such feature of SD-WAN is traffic segmentation. By segmenting the network, traffic cannot easily jump from one sub-system to the next and this barrier optimises the network to limit the impact that any security breach may have on the network. Another optimisation is that to prevent breaches, technologies such as encryption and SSL/TLS have been implemented. Both of these features protect sensitive data by cryptographically obscuring it and this improves the integrity of the network by allowing only those authorised to access it.
Advanced Reporting Capabilities
SD-WAN improves the reporting capabilities offered by traditional WAN systems.
One example of this is the data analytics that are provided from the application, routing and path-selection process. SD-WAN can monitor traffic directly from the application-level, to see which applications are using the most bandwidth, whilst also displaying how different network links are being utilised, if any jitter is experienced and where latency is experienced within routing.
The security built in to SD-WAN is another example of this, as there are many ways to monitor the security of the SD-WAN network. In the event of a breach, SD-WAN provides advanced threat detection. This includes firewalls, deep packet inspection, malware scanning and real-time data feeds to ensure that no malicious traffic can traverse the network undetected. SD-WAN also uses AI and ML algorithms for anomaly detection, indicating potential threats to the network. By allowing for proactive mitigation, SD-WAN enables administrators to rapidly respond to network threats by providing a single security update ahead of any issues, that will then be pushed to all devices in a consistent manner.
These advanced reporting capabilities allow network administrators to get an overview, see utilisations and the security of their network, allowing for more-informed network improvements.
Cost Efficiency
SD-WAN can be considered a cost-efficient networking architecture in comparison to more traditional WAN networks (using MPLS). As SD-WAN is able to leverage multiple ISPs (broadband, 4G, 5G, LTE, internet leased lines and satellite services) and combine them for greater bandwidth, SD-WAN enables businesses to use cheaper services whilst still maintaining optimal network performance for crucial applications.
Furthermore, as MPLS systems require manual configuration for routing protocols and of failover/redundancy. SD-WAN automates these processes, saving on labour costs.
Why IT Decision Makers are switching to SD-WAN
As seen by Pfeifer & Langen Polska, SD-WAN was able to significantly cut WAN operational costs by 40%. These cuts were made by setting up a traffic filtering policy between OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and OMP (Overlay Management Protocol) as the central policy in the SD-WAN setup. Pfeifer & Langen Polska highlighted the flexibility of their SD-WAN solution allowed their company to negotiate better with their connectivity providers. The network’s independence from these providers meant they could consider other options without affecting the WAN infrastructure.
Operational costs are not the only factor that SD-WAN benefits. Solenis, a global presence in over 100 countries, faced significant challenges with their network infrastructure. These challenges ranged from slow file transfers and delayed database syncing to poor application performance and this was hindering critical business processes across order management and delivery. Solenis used SD-WAN in order to resolve these issues through Aryaka’s proprietary byte-level data deduplication algorithm, Advanced Redundancy Removal (ARR™). This significantly improved network throughput by removing redundancy from WAN traffic. This has led to bandwidth utilisation reductions of up to 99% and a decrease in round trips by as much as 95% in some customer deployments.
SD-WAN fundamentally transforms an organisation’s network architecture through numerous ways. From improved routing efficiency to simplified management, direct cloud access to enhanced security using AI and ML, SD-WAN proves to be an upgrade on traditional WAN architectures that IT decision makers should consider. When considering SD-WAN, it is recommended that IT decision makers carefully evaluate all features offered by each vendor, as each solution can offer different benefits towards costs, security and efficiency issues. The best way to do this is to use the Netify 2024 SD-WAN Comparison.


