| SD-WAN benefits manufacturers by enhancing network reliability, reducing downtime, and improving security with Zero Trust Architecture (ZTNA). It simplifies deployment, scales operations, and optimises performance. |
Manufacturing businesses are switching from traditional Wide Area Networks (WAN) to Software Defined Wide Area Networks (SD-WAN) with the incentive of decreasing network downtime, improving security and enabling greater agility and scalability for operations. SD-WAN mitigates many of the issues found within traditional WAN networks, which can offer business with improved efficiency and reduce costs.
Enhanced Network Reliability and Uptime
One issue that businesses typically find with their traditional network routing is that it relies too heavily on static paths and legacy protocols, which can lead to traffic-flow bottlenecks, single points of failure and traffic degradation. Within the manufacturing sector these limitations not only slow processes but cause loss of revenue due to system downtime or delayed operations, such as where a single communication link becomes overwhelmed by traffic, forcing a production line to pause operations.
According to a study by ITIC, an hour of downtime can cost manufacturing companies between $100,000 and $1 million, depending on the scale and type of operations, further emphasising just how important networks are to daily processes. Where manufacturers rely on data transfer across a network for production operations, even a brief outage can be catastrophic and therefore properly managing the network is integral to the business.
This issue is addressed by dynamic path selection, the adaptable routing feature built into SD-WAN. By leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI), SD-WAN monitors the health of all communication links in real-time and network traffic is automatically routed via the best performing available path. Switching between network paths is entirely seamless without any noticeable impact for affected systems, which is ideal for manufacturers with strict production schedules. This ensures that performance and reliability is optimised, which assists in the prevention of potential outages to critical processes for manufacturers.
Centralised Management and Simplified Deployment
Businesses often find that managing a traditional network can involve multiple different systems with lots of manual configuration. This leads to network administration inefficiencies and increased complexity, especially for businesses that operate with network devices across multiple geographical locations that need on-site maintenance. Unfortunately, this can slow down the process of commissioning new facilities or production lines as scaling requires constant manual work from network administrators on-site.
To improve the agility of businesses, SD-WAN offers a unified platform to manage the entire network, including remote sites, from a central location. This simplifies network management and deployment by allowing network administrators to configure and maintain the entire network from a single remote dashboard. For manufacturers this facilitates operational scaling, enabling rapid setup of new production lines or facilities without manual work on-site.
By improving scalability of the network through centralised management, this translates to increased profits and significant time and cost savings. This is achieved by reducing the need for on-site network administrators, reduced setup times and the ability to adapt to changing market demands with minimal disruptions. This operational efficiency improves business agility and optimises resource utilisation whilst reducing overhead costs. These benefits are reflected by reports that show efficient network management can reduce operational expenses by up to 30%, which can have a dramatic impact on budgets.
Improved Security with Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture with SD-WAN
Traditional network architectures are known to often face great difficulties when meeting the criteria for compliance with regulatory requirements. These difficulties come as a result of perimeter-based network defences and a lack of granular access controls for network traffic. Security is essential for networks as these set out how to protect sensitive manufacturing data and Operational Technology (OT) systems, which are critical for maintaining production integrity.
As manufacturers continue to integrate Internet of Things (IoT) devices into their operations, the missing features from traditional networks become even more pronounced. IoT devices often have varying security capabilities, which, when deployed across a vast range of geographical locations, introduces the network to many new vulnerabilities. Gartner predicts that by 2025, 75% of industrial enterprises will use IoT devices, therefore these issues should be addressed to accommodate this shift.
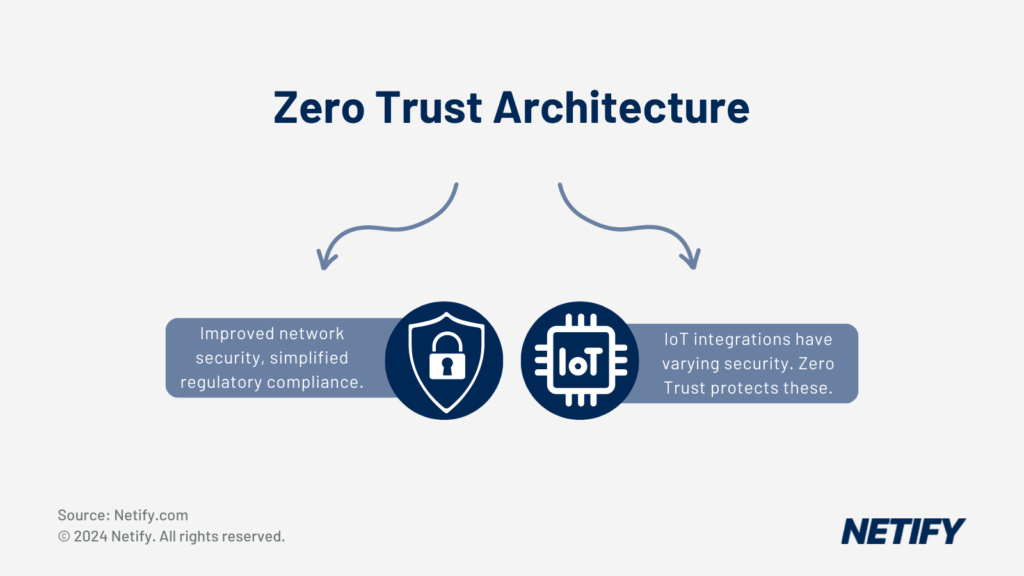
To provide improved security, one component of SD-WAN is Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA). Unlike traditional networks, ZTNA is based on the principle of “never trust, always verify”, ensuring that only authenticated users and devices can access the network. ZTNA continuously requires the user and device to be verified, segmenting network traffic to prevent lateral movement of threats within the network. For manufacturing environments, this segmentation helps minimise the attack surface, preventing multiple Operational Technology systems and sensitive data being breached.
Individual security alternatives to SD-WAN for IoT, such as standalone firewalls and intrusion detection systems, can offer some protection but often lack the integrated, scalable approach that SD-WAN with ZTNA provides. These alternatives may also require significant manual configuration and management, further complicating the integration process.
By leveraging ZTNA, SD-WAN not only improves network security but also simplifies compliance with regulatory standards. This integrated security approach ensures that manufacturers can protect IoT devices while maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of their operations.
Optimised Performance for Critical Applications
Another key feature of SD-WAN solutions are the integrated WAN optimisations for enhancing the performance of critical applications. Prioritisation of traffic is achieved through Quality of Service (QoS) functionality, ensuring bandwidth is allocated to most important applications, minimising latency and maximising throughput of traffic.
For manufacturers, applications such as Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM), are essential for design and production. These applications require high bandwidth availability and low latency in order to function efficiently, enabling real-time collaboration and seamless production line operations.
SD-WAN can also leverage multiple transport links, such as broadband, LTE and MPLS. This enables seamless distribution of network traffic to optimise link usage and allows critical applications to be segmented on their own traffic link to reduce interference from less important traffic. This ensures that, even during peak usage, performance remains consistent and reliable.
It is reported that a leading manufacturer that heavily relied on CAD/CAM software implemented SD-WAN to improve issues with congestion and latency within the network. The company was able to significantly reduce latency and improve bandwidth for critical applications, with a 30% improvement in application performance and a 25% reduction in production cycle times. This led to a substantial cost saving and increased productivity, showcasing the offerings of SD-WAN to improve operational efficiencies.
Scalability and Flexibility
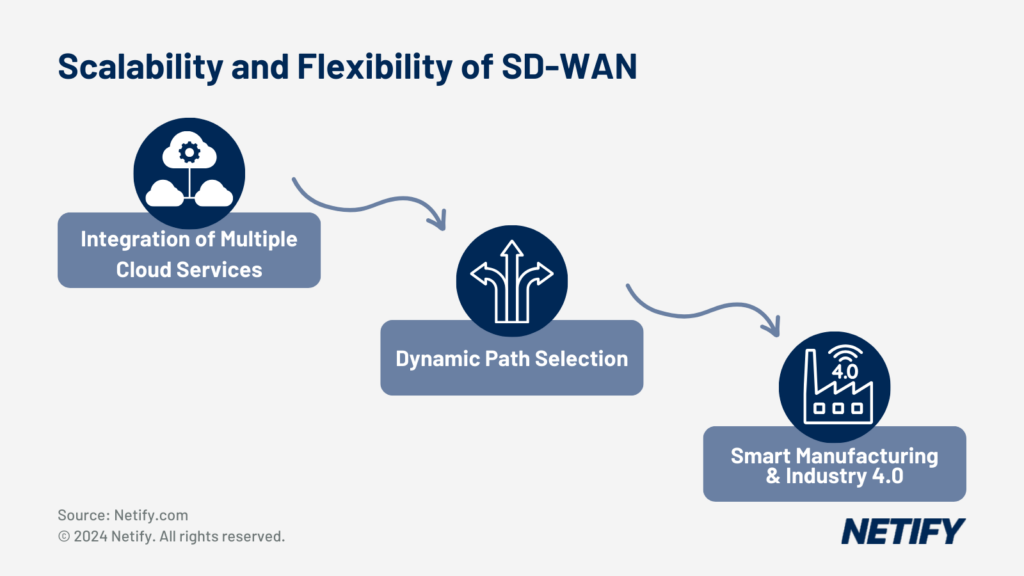
With many manufacturing businesses integrating cloud services for a flexible and scalable network architecture, there is a greater importance on managing these connections. SD-WAN is capable of managing multiple cloud services, enabling manufacturers to benefit from the unique offerings of each cloud service provider. This also facilitates utilising multiple cloud backbones to improve path selection capabilities for improved performance, whilst not-being tied to a single cloud provider also prevents vendor lock-in, improving flexibility to the network.
Scalability and Flexibility of SD-WAN
The scalability and flexibility provided by SD-WAN are particularly beneficial for the dynamic needs of smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 initiatives. These are utilised for the integration of AI, robotics and IoT in order to automate and optimise the production process. By supporting these integrations, SD-WAN improves network scalability and flexibility by enabling manufacturing businesses to scale resources or production lines at ease, without constraints being imposed by the network architecture.
Cost Efficiency
Cost efficiency is often one of the most important aspects within manufacturing businesses and that should extend to the network as well. Traditional networking solutions often rely heavily on Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) links, which, while reliable, are expensive and can strain IT budgets. SD-WAN, on the other hand, allows manufacturers to leverage more cost-effective broadband connections without compromising on performance or reliability. This reduction in reliance on costly MPLS links results in substantial savings and improving both Operational Expenditure (OPEX) and Capital Expenditure (CAPEX).
Case studies reflect these savings with a global manufacturer reporting a 50% reduction in network costs after switching to an SD-WAN solution. This enables the organisation to reinvest the savings into their production facilities, improving operational efficiency and expanding their product lines. This means that the switch to SD-WAN directly assisted in the company increasing their market share.
Enhanced Visibility and Control
For businesses lacking visibility or insights into their network, SD-WAN offers the solution. Through real-time analytics and network health monitoring, SD-WAN provides live insights about the network, such as common traffic patterns, bandwidth usage, security threats and even device performance. By providing them with increased visibility and control, network administrators can proactively manage their SD-WAN network, monitoring and mitigating any unexpected disruptions or outages. This ensures that production processes aren’t halted, therefore minimising loss of revenue.
The ability to monitor network performance in real-time significantly improves operational efficiency. Network administrators can quickly identify bottlenecks, optimise traffic flows, and ensure that critical applications receive sufficient bandwidth.
Finally, improved visibility and control helps manufacturers to discover security vulnerabilities, detect and respond to threats, reducing the risk of data breaches. This endured that sensitive manufacturing data and intellectual property are protected, assisting manufacturers with regulation compliance.
Conclusion
SD-WAN is an essential tool for any businesses in the manufacturing sector that require improved network reliability, centralised management or simplified scaling and deployment. With features such as dynamic path selection and ZTNA, manufacturers can minimise network downtime and improve security to enhance availability and confidentiality, whilst also complying with regulatory standards. The integrations of WAN optimisation and traffic prioritisation through QoS policies improve overall performance and ensure critical applications are given adequate resources to prevent degradation. SD-WAN also supports Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing, enabling the shift to utilising technologies such as AI and IoT, whilst also supporting multi-cloud, improving cost efficiencies for the network through operational savings.
Compared to traditional WAN networks, SD-WAN provides manufacturers with the ability to achieve efficiency, agility, and resilience with their network.


