| Top SD-WAN capabilities include performance and security improvements, cloud support integrations and increased cost-efficiency. |

When evaluating the infrastructure for their network, IT decision makers must consider the capabilities of Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) solutions and how its benefits outcompete those of less-refined, traditional networks.
Table of Contents
Advanced Traffic Management
For many organisations, the most important network metric is performance. SD-WAN is capable of improving network performance, whilst also reducing costs through techniques such as dynamic path selection and Application-Aware Routing (AAR).
Dynamic path selection enables SD-WAN to intelligently distribute network traffic over multiple WAN connections, such as MPLS, internet broadband and cellular. To achieve optimal path selections, SD-WAN analyses real-time telemetry data from the network. SD-WAN can detect if a network links is underperforming by comparing current network telemetry to historical data. Once problem areas are identified, SD-WAN can rectify the network before issues such as degradation can take effect. By seamlessly and proactively switching between network paths, SD-WAN ensures critical application uptime is maximised, improving the overall user experience (UX) when compared to traditional WAN networks.
Traffic is analysed to detect the source application and its importance to the organisation. Known as Application-aware routing, this capability is leveraged within SD-WAN and uses Quality of Service (QoS) policies to assign importance. QoS policies define the priority level of all applications and traffic, ensuring that higher priority applications receive adequate bandwidth and network resources. This minimises the risk of traffic degradation for business-critical applications and so applications such as Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) are routed via the lowest latency path, whilst bandwidth-intensive applications are segmented and routed across paths with high bandwidth availability.
Enhanced Security Features
To protect business-critical applications from downtime, networks require comprehensive security. SD-WAN integrates security frameworks, such as Secure Access Service Edge (SASE). SASE introduces consistent security across all connections regardless of device or connection type. SASE security features include firewalls, Secure Web Gateway (SWG) and Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA). These enable organisations to utilise the cloud.
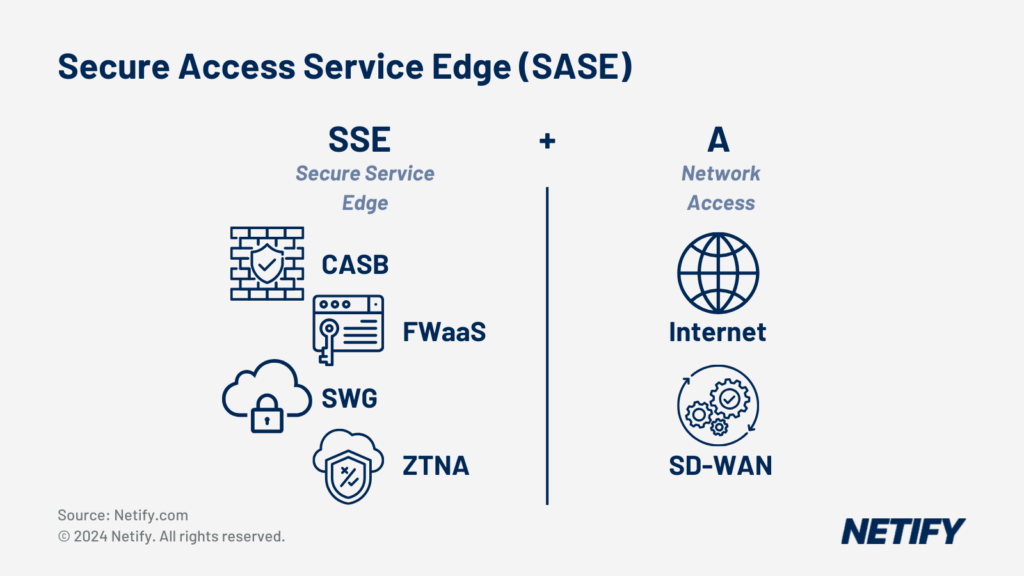
Security features such as botnet intervention and anti-malware systems, found in next-gen security devices, are also being integrated which ensure that the security policies are consistent, up-to-date and increases the overall protection for a system.
AI-Driven Automation and Orchestration
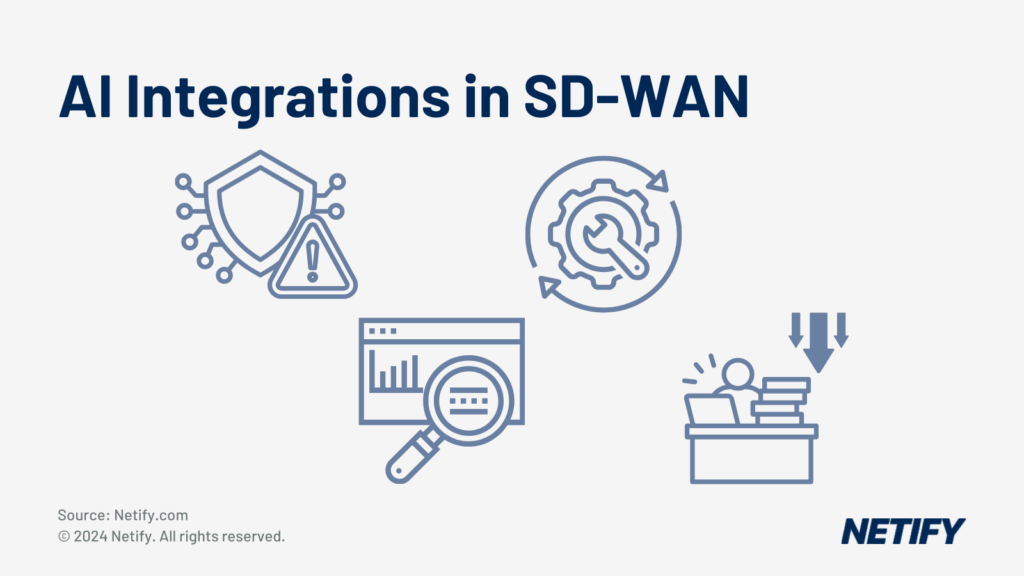
However, IT decision makers may be concerned that the addition of so many security features may require lots of manual work to manage. To reduce workload, SD-WAN is increasingly using Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), with AI evaluating real-time network telemetry data, analysing patterns to find anomalies and detecting performance issues or threats before they have even affected the network. This enables the SD-WAN orchestrator to provide proactive responses to problem network areas, optimising network efficiency and user experience (UX).
The ability to use predictive analytics can also be leveraged by Artificial Intelligence in order to manage threats to security. This allows the SD-WAN orchestrator to automatically trigger security controls in order to manage potential threats.
Optimised Cloud Connectivity
As SD-WAN often integrates network security via the cloud, there is no longer the need to transfer cloud-destined traffic via a central data centre and thus direct cloud connectivity can be utilised. SD-WAN enables cloud connections via on ramping capabilities, simplifying the creation of direct connections from branch offices to the cloud, reducing the need to backhaul data to a central data centre, as is used in traditional WAN solutions that make use of MPLS.
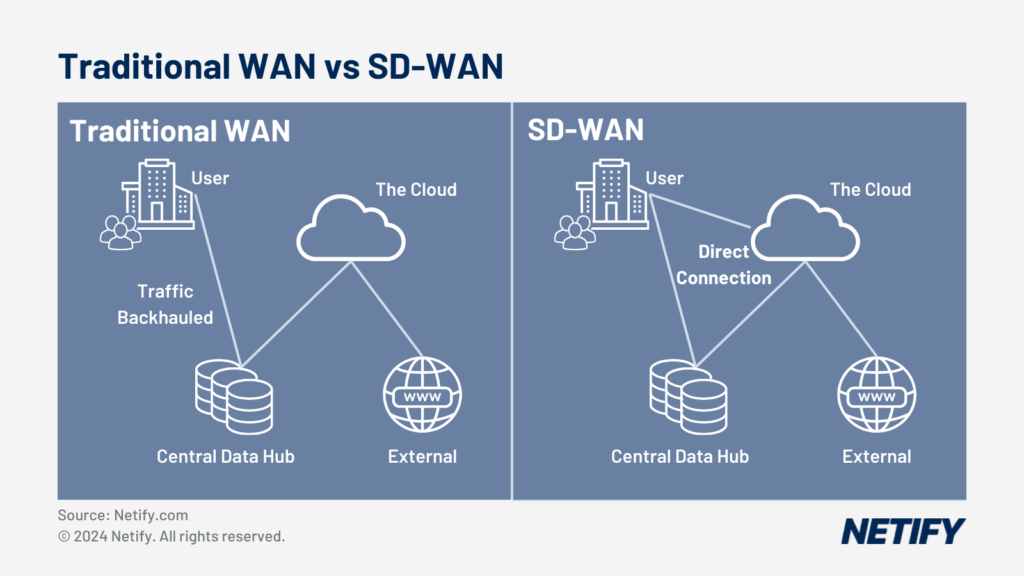
Due to the ability to create direct connections from users to the cloud, SD-WAN is therefore particularly applicable in organisations utilising Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS).
As multi-cloud is a popular trend, where networks leverage multiple cloud providers services, network administrators can deploy SD-WAN within AWS, Azure and Google Cloud Platform, routing traffic across each cloud providers backbone in order to gain high performance connections.
Edge Computing Integration
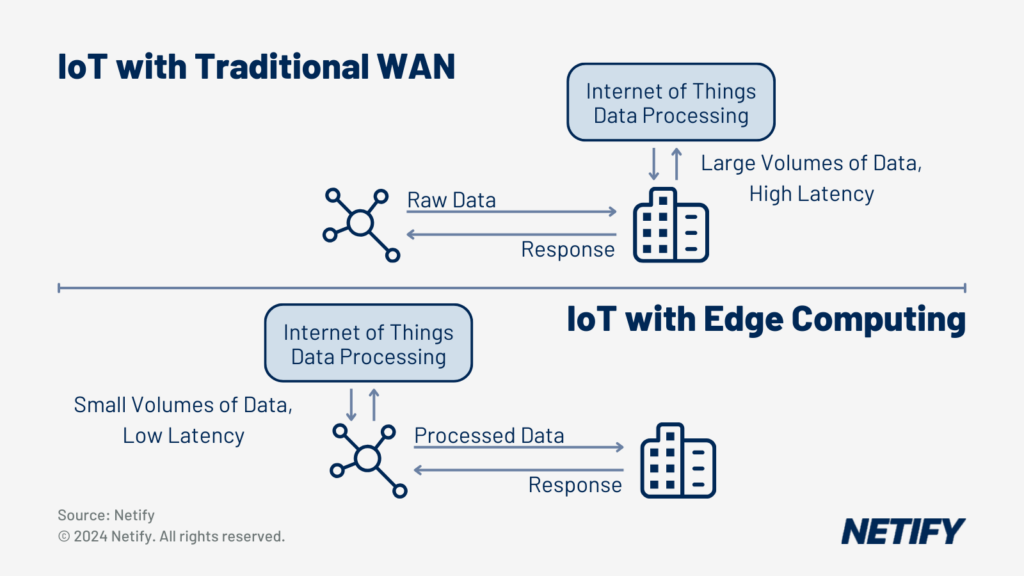
To integrate cloud connections effectively, the processing delay of services being routed across the network require minimising. SD-WAN enables Edge Computing, a network architecture where user traffic is processed as close to the user as possible, rather than routing data to a central data hub. Edge computing can be important for technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT). By processing data closer to the source, this reduces latency, improving application performance and optimising bandwidth utilisation. SD-WAN also provides additional security capabilities for edge resources, ensuring that these devices integrate with the wider network policies and improves the confidentiality of data processed at the network edge.
Enhanced User Experience
To increase your businesses productivity, it’s important to improve user experience. SD-WAN can use Quality of Service (QoS) to optimise network performance by monitoring traffic across latency, jitter and packet loss. If any of these areas experience issues (by breaching a set threshold), SD-WAN will adapt by choosing an alternative path, perhaps over a secondary leased line, Broadband or cellular. The setup of QoS included traffic shaping and prioritisation, which helps build in flexibility and reliability.
Within SD-WAN, the ability to optimise network performance is enabled by separating the network control plane from the traffic plane. This separation allows SD-WAN to provide network administrators with a centralised management pane for configuring consistent, universal changes to the network.
Scalability and Flexibility
Not only does centralised management improve performance but it also allows the network to be scalable and flexible. This reduces the amount of manual configuration required to deploy and maintain the branch offices, which may be at distributed geographical locations, whilst universal policies mean that on-premises, remote or hybrid workforces receive a consistent experience when using the network.
Another way that SD-WAN offers scalability and flexibility is through leveraging a multi-cloud system. This means that the benefits of each cloud service can be utilised, such as differing geographically located backbones, whilst not being tied to a single vendor. By combining the benefits of multiple cloud services, SD-WAN ensures performance and user experience is optimised. Through a technique known as ‘elastic scaling’, cloud resources can be dynamically enabled based on cloud demand from the network. When multiple cloud services are used, scaling can be performed at each cloud provider, so that SD-WAN can get the best service possible whilst reducing costs.
Comprehensive Network Visibility

The centralised management pane also enhances visibility into network metrics. This telemetry data enables network administrators to monitor performance and security in real time with detailed insights. These features are typically being supplemented by Artificial Intelligence, where anomaly detection and root cause analysis are used to provide rapid resolutions and either a notification or insight is provided to network administrators, reducing their workload.
Cost Efficiency and ROI
SD-WAN reduces the reliance on dedicated MPLS circuits. This is due to the capability to leverage multiple transport links such as cost-effective broadband, with optimised bandwidth utilisation for improved performance.
Case studies have shown organisations switching to SD-WAN have often reduced costs by 40-70% whilst gaining the agility, performance and security benefits of SD-WAN. This means that there is a high Return on Investment (ROI).
Future Trends and Innovations
The integration of 5G communication links improve network speeds for SD-WAN, whilst Artifical Intelligence can be leveraged for path selection and security features. Meanwhile, the usitilisation of Edge computing enables processing to be actioned closer to the source and these improvements combine to maximise network performance improvements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SD-WAN provides many benefits over traditional network infrastructures. Improvements include performance, security and cost efficiency, which are enabled through advanced traffic management capabilities, application aware routing, AI-driven automations and edge computing.
Cloud integrations enable organisations to leverage distributed workforces, providing consistent user experiences, regardless whether users are located on-premises, fully remote or hybrid. By supporting remote workforces, SD-WAN with cloud integrations also caters to the growing demands for Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS). Finally, cloud integrations also include multi-cloud utilisation, where benefits such as different geographically located global backbones can be used for increased network performance.
Cost efficiency and high ROI are significant benefits of SD-WAN over traditional WAN networks. Through the capability to leverage multiple network transport links, SD-WAN not only enables the usage of more cost-effective broadband connections but also benefits organisations with improved agility and performance. As 5G and AI become more and more integrated into SD-WAN solutions, the cost efficiency and performance improvements of SD-WAN are only anticipated to increase, indicating an ever-improving infrastructure design.
It is therefore important for IT decision makers to consider SD-WAN for their network infrastructure due to the significant benefits over traditional WAN, reducing reliance on dedicated MPLS circuits and an increased ability to future-proof the network. However, as SD-WAN vendors offer differing solutions, we would strongly recommend IT decision makers read our SD-WAN comparison guide.


