The Top 7 Concepts of SD-WAN are:
|
Working across SD WAN services, you’d think we’re in a world where networking issues simply do not exist. I’m expecting to read that Einstein was simply wrong about the laws of physics because the latest Software-defined WAN capability has broken the speed of light.
Perhaps we’ll be at the stage where WAN optimisation knows the data you’re about to generate before you’ve even thought about pressing send? In short, the sarcasm above really does demonstrate the advances we are all experiencing across end to end data delivery from the LAN and WAN through to Data Center and Security. We do need to remain grounded when considering SD WAN benefits; networking performance remains fundamentally attached to latency and jitter. With this said, significant advances are regularly occurring, which offer the average Enterprise business the ability to leverage the Internet with consistent networking performance. As providers and vendors continue to innovate, Netify is working hard to keep our research up to date and relevant to help the decision-making process of Global IT teams.
In this article, we’ll discuss 7 SD WAN concepts to help readers clearly understand where some of the main benefits exist and how they are positively impacting telecoms innovation.
1. Using SD WAN over the internet costs less.
The concept of TCO (Total cost of ownership) reduction is perhaps the most prominent marketing strapline you’ll read as your business investigates the benefits and concepts of SD WAN. And while Internet circuits (or public IP if you prefer) are cheaper vs MPLS, there are countries where the difference is less impactful to your bottom line. In the US, MPLS is much more expensive vs Internet whereas, in the UK, the costs are more aligned. In some instances, the TCO & ROI (Return on Investment) conversations need to go deeper into less obvious savings such as improved security or capability to leverage multiple circuit types which in turn increases uptime and avoids costs to the business when downtime occurs.
SD WAN appliance pricing varies significantly between provider, differences occur depending on feature capability, brand and proposition. Solutions are available with private PoP backbone access which will increases costs vs an Internet-only variant. While certain providers & vendors will deliver the SD WAN concept as an all-encompassing solution, careful thought should be given to the direct benefits. Whether or not you need full capability requires aligning your specific requirements to corresponding features.
Today, the Internet is a well-scaled viable WAN infrastructure platform for transmitting mission-critical data between host and users. We’re seeing the decline of layer 3 MPLS VPN in part due to public Cloud-based applications access but mostly because the Internet offers comparable performance with the addition of SD WAN traffic optimization features.
2. SD WAN solutions offer more bandwidth.
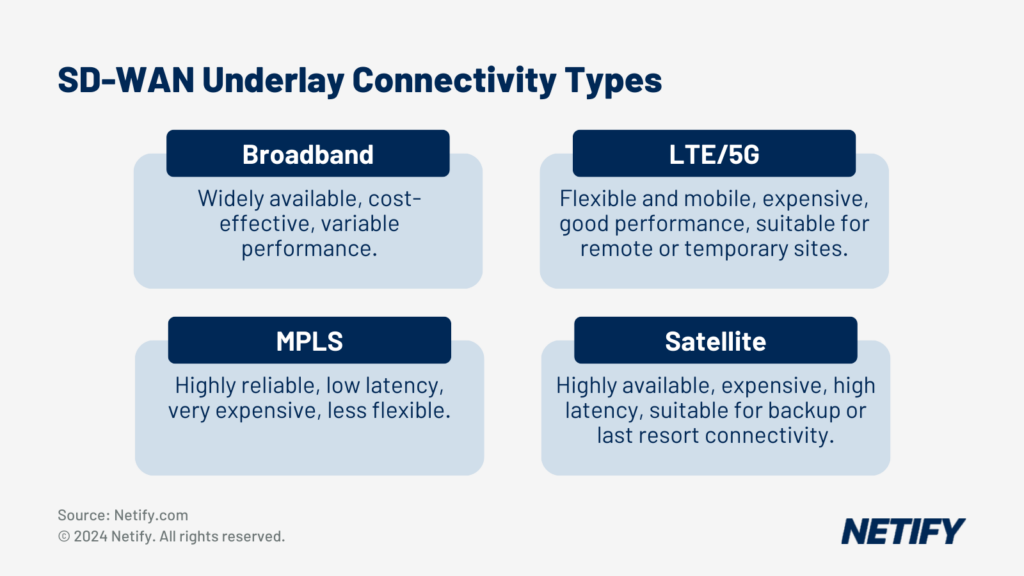
The ‘increased’ SD WAN bandwidth concept is the result of path selection across not only primary Ethernet but Broadband, 4G and 5G connectivity. Where required, less mission-critical applications are routed via lower-cost connections. As an example, general Internet browsing could be made to use low-cost Broadband circuits, whereas Voice, Video and other critical applications are sent over better-performing Ethernet circuits.
In some cases, per session load balancing might be appropriate and, where similar circuits are concerned, load balancing in this way provides the most effective form of making the best use of your bandwidth. Note that per packet would not efficiently work across circuits with variable latency and jitter.
3. SD WAN consolidates multiple technologies into one solution.
SD WAN is attempting to end the concept of buying LAN and WAN technologies as a silo based purchase. With next-generation firewall security, support for multiple connectivity technologies, WAN optimisation and reporting there is the capability to deliver every element of your WAN in a single device. Technologies from Cisco Meraki include CCTV support with specific application functionality which helps businesses with physical security and not just the network.
The concept of SD WAN function consolidation (stat provided by Cisco) suggests that an individual network engineer is responsible for maintaining approximately 200 devices. The Cisco stat goes on to mention an example of 30 IT operations staff managing 6000 concurrent devices. The reason for mentioning such statistics is that devices are growing, think phones, tablets, and so forth. With this in mind, simplifying the network and applying policies from a central software-based location means the aforementioned devices are easier to maintain.
4. SD WAN architecture allows better access to cloud services.
Cloud technology (SaaS applications) is one of the primary reasons for the growth in Software-WAN adoption. Access to AWS (Amazon Web Services), Microsoft Azure, Office 365 and Google Cloud are all examples of cloud services which are easily accessed over the public Internet. Remote working from multiple devices across the Globe in a secure environment is made possible by SD WAN VPN access.
In addition to the availability of Internet connectivity, path selection based on traffic performance characteristics is one key advantage of SD WAN solutions. In a traditional routed legacy WAN, traffic routing between sites or data center locations remained static because the routing control function existed within the edge device and not centrally via management servers.
5. SD WAN offers the ability to virtualise network functions.
SD WAN is available as a virtual instance. The concept of NFV (Network Function Virtualisation) offers the opportunity to move away from the dedicated WAN edge customer premises device to automation and orchestration. There are two areas discussed within Sofware-WAN virtualisation topic.
- NFV (Network Function Virtualisation)
- VNF (Virtual Network Virtualisation)
In a VM solution, several Virtual Network Functions are run at the same time but isolated from each other to form standards-based functions which offer the ability to independently upgrade.
The advantages of NFV surround the ability to quickly deploy new services to branch offices and remote sites with reduced dependence on hardware. Within the flexibility of NFV, services can easily be scaled up and down together with the capability to upgrade NFV services independent of the hardware.
The difference between NFV and VNF is subtle in respect of NF (Network Function) controlling the overall rollout of virtualised network services and FV (Function Virtualisation) as the actual service or feature.
6. The concept of no longer requiring Managed SD-WAN services.
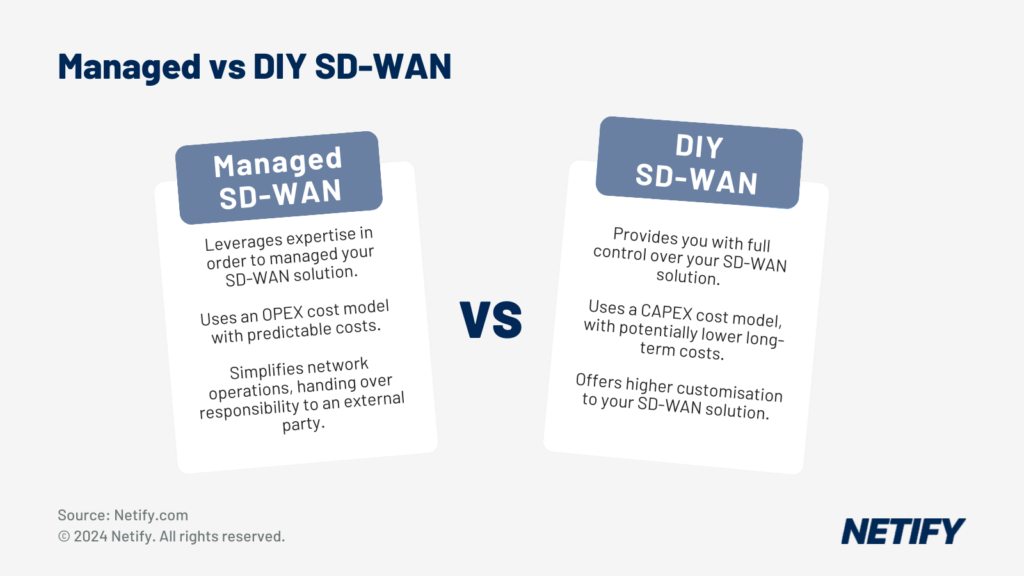
One major difference between legacy WAN edge-based networks vs SD WAN is across the management interface. With traditional routers, the command line style of management required significant expertise to provision and maintain. The major shift created by Software WAN concepts surrounds the almost plug and play capability of WAN deployment. The level of knowledge required varies between each vendor with certain deployments requiring more expertise, Cisco Viptela is a good example. When reviewing the vendor marketplace, other solutions offer plug and play features including application databases with QoS ready profiles.
In terms of day to day management, the GUI (Graphical User Interface) approach makes configuring, changing and viewing network details much simpler vs legacy routers. Regardless of how SD WAN is simplifying deployment and management, the knowledge of networking and security is required to make the right decisions. With this statement in mind, co-managed services are becoming popular, dealing with initial consultation across aspects such as security policies.
7. The concept of QoS (Quality of Service) over the Internet.
While SD WAN cannot deliver the end to end Quality of Service of layer 3 MPLS or layer 2 VPLS, there are features to ensure traffic is delivered as required. With an end to end QoS deployment, there is the confidence traffic will be delivered with priority based on EF, AF and Be traffic profiles. The performance of legacy QoS becomes less effective when the network experiences degradation such as packet loss, high latency and jitter.
SD WAN maintains high availability and application performance by sensing issues and making decisions on alternative routes using application steering, packet duplication and FEC (Forward Error Correction). Packet duplication allows other links/circuits to be used (4G, 5G, Broadband) when the primary path experiences issues. In this scenario, the duplicated packet is sent dynamically over an alternative path resulting in seamless data transfer.
- Both circuits/paths must be up and operational (clearly!)
- One of the circuits/paths must be experiencing loss/issues to trigger the threshold
- Both paths/circuits must offer roughly similar latency, or the issues could be compounded
With packet-based FEC, SD WAN is able to reconstitute lost packets at the far end of a WAN connection, avoiding typical delays that come with round-trip retransmissions.
8. The concept of next-generation security.
Vendors often lead from a core capability, perhaps WAN optimisation or Security was/is their core capability. While advanced routing, traffic optimisation are critical tenants of the overall proposition, Security is the number once concern across all Enterprise businesses considering WAN solutions today. Next Generation Firewall Security (NGFWs) as an SD WAN concept brings all aspects of the WAN experience together into a single solution. While performance and uptime policies exist for application traffic, Security can also form a key component of the way in which your overall policies co-exist as offering a complete end to end solution.
Next generation security components typically include:
- Application awareness
- Integrated intrusion prevention systems (IPS)
- Identity awareness, user and group control
Conclusion
The concept of SD WAN is based around the centralised management of network functions away from the WAN edge, the ability to steer cloud applications & traffic with QoS, next-generation firewalls & associated security, simplified management and NFV. While there are undoubtedly other concepts, these features represent the most discussed topics.
In the majority of cases, SD WAN often includes hybrid networking resulting in a combination of connectivity services including MPLS, VPLS, private circuits and Internet to meet the overall requirements of your WAN solution.


