| CASB solutions differentiate vendors by features like data loss prevention, malware detection, encryption, threat prevention and regulatory compliance, ensuring secure cloud access. |
What is CASB?
Gartner (2022) defines Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) as “on-premises or cloud-based security policy enforcement points, placed between cloud service consumers and providers to combine and interject enterprise security policies as the cloud-based resources are accessed.”Cloud Access Security Brokers are contact points bridging the gap between the traditional network and cloud resources. CASB was initially designed to combat Shadow IT threats but has evolved to meet the needs of cloud computing, cloud data storage and BYOD policies by providing consistent security policies across multiple clouds. CASBs offer unique security features not found within other security controls, such as Secure Web Gateways (SWG) or enterprise/web application firewalls, ensuring its place as a critical element of enterprise security.

- What Is Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)?
In this article, we will break down CASB into these security features that differentiate the strengths and weaknesses of vendors and managed service providers. The following security features are some of the components available through a CASB solution; however, depending on the vendor or service provider, the offering may vary.
Data Loss Prevention
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a set of tools and processes that allows an administrator to control the data that users can transfer and prevents potential data breaches by monitoring, detecting and blocking the transfer of critical or sensitive information to recipients external to the corporate network.
Configuration Auditing
Configuration auditing offers tools that compare detected changes, configuration assessment and reconciliation of changes against approved requests for changes (RFCs) and mitigation. In an organisation using company-specific policies or security configuration assessment templates, CASB can assess configuration settings for security hardening and auditing. The tools focus on PC and server requirements, though administrators can use some for databases, network components, applications and virtual infrastructures.
SSO and IAM Integration
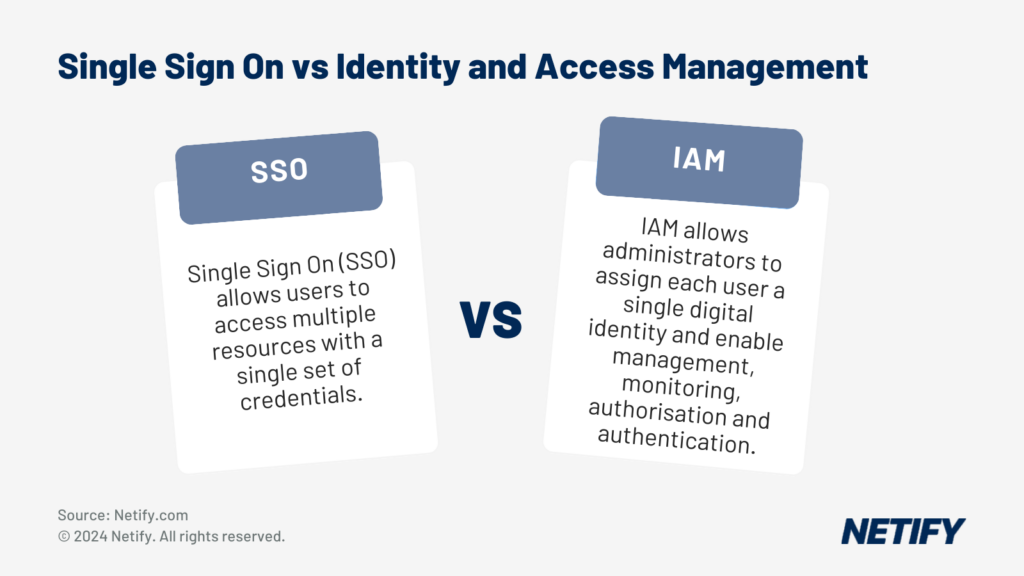
Single Sign On (SSO) vs Identity Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management, as defined by IBM (2022), is “the security discipline that makes it possible for the right entities to use the right resources when they need to, without interference, using the devices they want to use”. Single Sign On (SSO) allows users to access multiple resources with a single set of credentials. IAM stands between users and critical enterprise assets and allows administrators to assign each user a single digital identity and enable management, monitoring, authorisation and authentication. IAM helps to identify compromised credentials or weak user passwords. A good CASB will allow for integration with SSO and IAM facilities.
Cloud Governance and Risk Assessment
CASB provides a centralised view of the cloud environment, with cloud services catalogued and assigned a score based on the service’s overall trustworthiness and risk level. CASB will then provide automated access controls based on parameters such as the cloud service risk score, data permissions and app category.
Malware Detection
Cloud Access Security Brokers help to limit the risk to an organisation by analysing and automatically remediating threats. CASB detects unusual behaviour across cloud applications and identifies compromised users, ransomware and rogue applications.
Data Encryption and Key Management
The Cloud Security Alliance (CSA, 2022) advises that there are three methods of encrypting cloud-based data. These are: Gateway delivered encryption, Bring Your Own Key (BYOK) encryption and vendor-provided encryption.
- Gateway-delivered encryption: Data is encrypted as it leaves the corporate network, with the vendor retaining no capability to access the data. CASB may integrate with a cloud-delivered key management solution or an enterprise’s key management solution through a Key Management Interoperability Protocol (KMIP).
- BYOK encryption: Encryption keys are generated and managed by the organisation, which the enterprise can share with the vendor. The vendor encrypts the data and retains the capability to access the data.
- Vendor-provided encryption: CASB is not involved; the vendor encrypts the data and retains keys, key management and the capability of accessing data. User interfaces issued by the vendor may provide administration.
Threat Prevention
Threat prevention is the ability to block specific threats before they cause damage or penetrate an environment. A CASB often delivers this as a User and Entity Behaviour Analytics (UEBA) solution. A UEBA solution monitors user behaviour and tracks user behavioural patterns. UEBA can assist in detecting potential threats by identifying discrepancies and anomalies in a user’s behaviour, offering additional protection from targeted attacks and insider threats.
Contextual Access Control
Contextual access control is a feature of firewall software which intelligently filters TCP and UCP packets based on application-layer protocol session information. Organisations can use contextual access control for intranets, extranets and internets.
Control of native cloud services features
CASB allows administrators to control native features of cloud services, such as collaboration and sharing.
CASB Use Cases
CASB Use Cases
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Use Case | Security Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 12:37 PM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 12:37 PM | Visibility into application usage | Control of native cloud services features |
| 2 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 12:37 PM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 12:37 PM | Added threat protection | Malware detection SSO and IAM integration |
| 3 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 12:37 PM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 12:37 PM | User behaviour analytics | Threat prevention |
| 4 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 12:37 PM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 12:37 PM | Compliance and data security | Data Loss Prevention Data encryption and key management Configuration auditing |
| 5 | hyelland | 29/10/2024 12:37 PM | hyelland | 29/10/2024 12:37 PM | Cloud application usage tracking | Cloud governance and risk assessment |
| Use Case | Security Feature |
CASB Deployment Options
A CASB is available in the cloud or on-premises, with most CASB deployments being SaaS-based. CASB supports three deployment models: API-Control, Reverse Proxy and Forward Proxy:
- API Control offers comprehensive coverage and rapid deployment whilst providing visibility into cloud data and threats.
- A reverse Proxy is suitable for devices not covered by traditional network security.
- Forward Proxy operates in conjunction with VPN clients or endpoint protection.
Proxy deployments ensure compliance with data residency requirements by enforcing inline controls in real-time.
Businesses should consider CASB products that offer various architecture options to cover all cloud access scenarios. Multi-mode CASB ensures the flexibility that companies require to expand their cloud security as their needs continue to evolve.
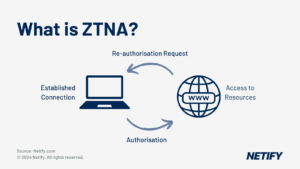
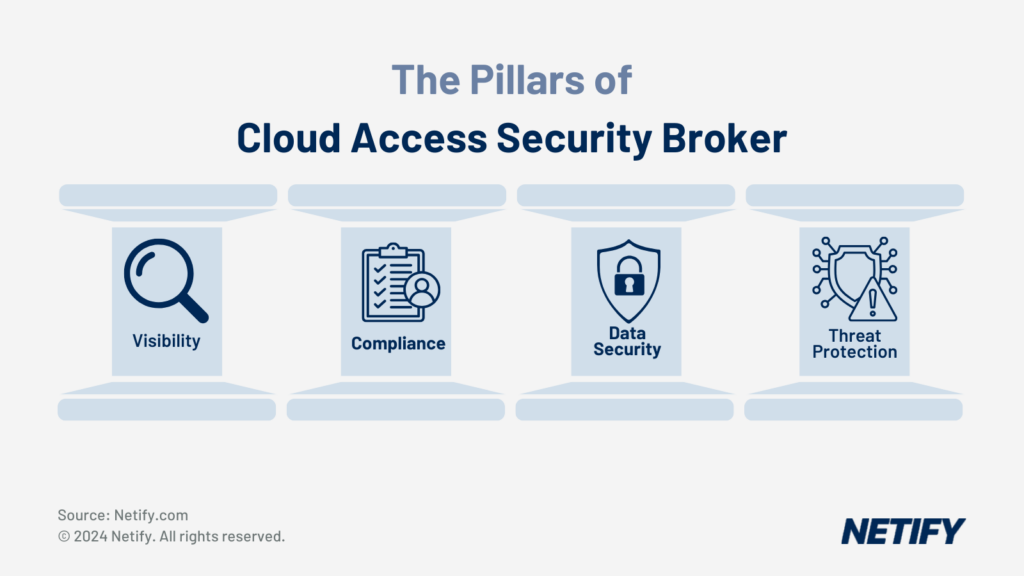
What are the four pillars of CASB?
- Visibility: Detection of suspicious behaviour by monitoring the usage of resources.
- Compliance: CASB usage ensures compliance with compliance regulations by providing the necessary tools and monitoring.
- Data Security: CASB security can include data discovery, encryption, remediation, access controls, permission management and tokenised data.
- Threat Protection: Identification and mitigation of internal and external threats.
What Is Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)?
Why is CASB important?
Cloud vendors focus on security at the infrastructure layer, which means that an organisation must implement risk mitigation at the business level to ensure the safety of users and data. The area at the network edge between the corporate network and third-party cloud applications is an appealing target for external threat actors. As attackers look to exploit vulnerabilities within an organisation’s third-party cloud services, the Cloud Access Security Broker is the first defence against cloud threats. Much akin to a drawbridge, the CASB identifies anomalous traffic to ensure the safety of the “walled garden” corporate network. The priority of the above CASB features will depend on the individual needs of the business. Determining the strength of a vendor’s CASB solution is dependent on how many of the features are included within the solution. The key benefits of CASBs according to Microsoft, 2022 are Risk visibility, Granular cloud usage control, Threat Prevention, Data loss prevention (DLP), and management & assessment of Shadow IT.
Conclusion
Though many vendors and service providers offer a Cloud Access Security Broker, it would be prudent to ask a potential provider what features their CASB would provide to see how a solution would align with your business needs. CASB is essential to modern enterprise security, and IT decision-makers should take care to ensure the best fit for your business.