| In 2024, SD-WAN offers the best way for businesses to move their network to smarter routing, improved security and cost savings over traditional WAN systems. |
Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) is a better way for businesses to manage their network across different locations. This is achieved by leveraging a combination of transport services, such as broadband, LTE/5G and allows a secure connection between users and applications. This replaces the need for expensive dedicated WAN connections and allows companies to build high-performance WANs using commodity internet connections.

What is SD-WAN?
The term SD WAN was coined by networking publications as early as 2014. Covering OSI Layers 4-7, SD-WAN is built on top of underlay connectivity and consists of four planes: Data, Control, Management and Orchestration. By acting as an intelligent WAN (Wide Area Network), it provides a direct link between cloud-based applications, branch offices and remote users with dynamic control of traffic pathing for traffic flow optimisation.
SD-WAN is a key component of the SASE framework, responsible for handling the secure underlying network architecture and connectivity that is imperative to SASE’s cloud-oriented approach. SD-WAN handles this by optimising the connection from branch offices and remote users to cloud applications and services.
Benefits of SD-WAN

Application Performance and Reliability Benefits
SD-WAN provides benefits that fundamentally change the way an organisation’s network is controlled, managed, optimised, and expanded.
SD-WANs have the ability to route traffic over several connection types such as MPLS, broadband, LTE and cloud, enabling data to be transferred via the most optimal path. This is extended by SD-WAN also being able to monitor real-time conditions of the network, prioritise crucial apps and therefore improve overall reliability of a system. This assists companies by combining multiple connections without interruptions to provide users with an increased bandwidth, increasing the overall reliability of the network and reduces the reliance on previously-used, specialised MPLS circuits. By reducing the need for specialised MPLS circuits, which tend to be costly, SD-WAN can also help save organisations on costs, providing a further benefit.
Another way that SD-WAN saves on costs is that it uses Virtualisation. Virtualisation removes the need for physical appliances as it is able to replicate functions such as firewalls, load balancers and WAN optimisation controllers on software-based virtual machines and thus eliminates the need for additional appliances. Virtualisation also allows for decoupling of the network control plane from the data plane, which enables centralised control and agile traffic management across the WAN. By doing so, businesses are able to utilise the direct-connection from branch offices to the cloud (which decreases latency). Businesses can also leverage lower-cost broadband internet connections for their WAN, reducing reliance on more expensive MPLS connections.
When considering control within an SD-WAN, Standardisation ensures the security, and manageability of SD-WAN solutions. It achieves this via Management and Orchestration, Quality of Service (QoS), Security and Interoperability:
- Management and Orchestration centralises the control of SD-WAN systems via software, allowing system administrators to efficiently deploy, manage and scale networks. This differs from prior solutions such as MPLS, which typically had fixed configurations and required physical adjustments to update the network.
- Quality of Service controls the performance of the network by classifying traffic by application, content type or source/destination in order to select the best routing and bandwidth allocation to optimise network performance.
- Security features are also implemented via Standardisation. Frameworks such as SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) enable cloud utilisation and are increasingly being adopted across different vendors. Security features such as botnet intervention and anti-malware systems, found in next-gen security devices, are also being integrated which ensure that the security policies are consistent, up-to-date and increases the overall protection for a system.
- Finally, interoperability means that standards are set for SD-WAN products so that they interconnect seamlessly, regardless of the vendor or solution so that there are no compatibility issues.
These features (amongst many others) change the way in which organisation’s network systems work in comparison to standard WANs with MPLS. By routing through multiple connections, optimising performance, enhancing reliability and reducing costs, SD-WAN provides an all-in-one solution to assist organisations improve on current systems.
SD-WAN Features and Descriptions
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | Feature | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:48 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:48 PM | Efficient Traffic Routing | Features application-aware routing (intelligent traffic system) over multiple connection types (MPLS, broadband, LTE). Uses the optimal path based on real-time conditions, improving network performance and reliability. Also combines multiple connections |
| 2 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:48 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:48 PM | Direct Cloud Connectivity | Enables cloud connections via on-ramping. This assists with rapid deployment of new sites and services. Cloud connections remove the need to route traffic via a central headquarters location, significantly improving system performance. |
| 3 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:48 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:48 PM | Data Optimisation | Features such as compression and caching reduce the amount of data transferred and optimises overall performance. |
| 4 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:48 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:48 PM | Centralised Management | Management systems improve network visibility for system monitoring and simplifies troubleshooting. This also allow for centralised configuration of systems and their policies via methods such as Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP). |
| 5 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:48 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:48 PM | Additional Security | Next-gen SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) features are increasingly being added, such as those found in Next-gen security devices, such as botnet intervention and anti-malware systems |
| 6 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:48 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:48 PM | Cost Saving | By leveraging cheaper broadband links in place of or in addition to MPLS, and reducing equipment costs through virtualisation and standardisation, SD-WAN saves overall cost of a system. |
| Feature | Description |
As these features vary from vendor to vendor, we would recommend checking out the 2024 Netify best SD-WAN vendor article to find the best vendor for your use case.
How SD-WAN Works
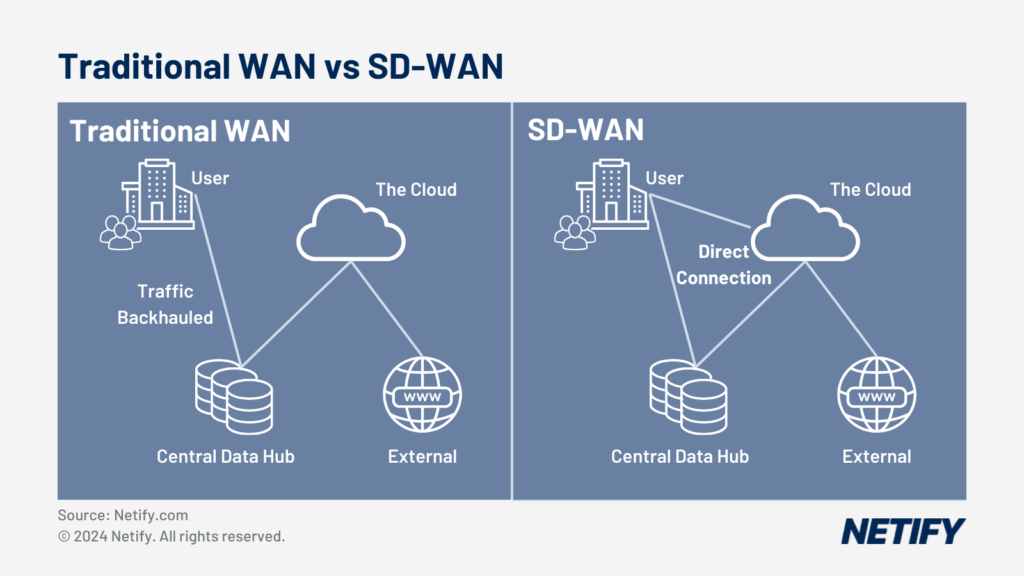
- Traditional WAN vs SD-WAN
SD WAN uses software to control and manage the interactions between branch and remote user locations and central resources hosted in a headquarters or data centre. Increasingly, enterprises are seeing the benefit of using the public Internet to enable employees to work from any device, anywhere in the world. SD-WAN is primarily composed of edge devices and gateway controllers:
SD-WAN edge devices
SD-WAN edge devices are deployed at branch offices or remote sites. These devices create a secure connection to the SD-WAN fabric (overarching SD-WAN system) and are in charge of enforcing policies and prioritising traffic within the deployed site. The SD-WAN edge device is also in charge of additional features such as integrating firewalls, performing routing and WAN optimisation.
SD-WAN gateway controllers
SD-WAN gateway controllers are deployed in data centres or cloud environments. These devices provide scalability and enable service chaining to deliver network services. These provide the control plane of the SD-WAN architecture, enable monitoring, policy management, are responsible for distributing policies to edge devices, monitor network performance and make dynamic routing decisions. The configuration for these are via an orchestration and management platform.
Routing
SD WAN can intelligently and coherently control the path of traffic to optimise traffic flow and choose the best data path transmission.
To facilitate intelligent routing and provide remote users with secure and reliable access to business-critical resources, many businesses have migrated the majority of applications to be hosted by public cloud service providers such as Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services (AWS). This has allowed SD WAN technologies to also leverage integrated security with real-time cloud intelligence.
SD-WAN vs Traditional WAN
SD-WAN is not just a “bolt-on” to traditional WAN systems but is an entirely new architecture with many added features and benefits. By enabling software defined networking (SDN), SD-WAN has the capability to move away from the expensive Multi-protocol Label Switching (MPLS) circuits previously used in traditional WAN setups in order to route traffic efficiently.
This efficiency is increased by SD-WAN offering the ability to dynamically route traffic, meaning that routing can be done based on real-time network conditions, unlike with MPLS circuits which are hardwired to route over set paths (which limits their ability to route as efficiently). This therefore reduces overall latency and provides a benefit of SD-WAN over traditional WAN for businesses.
As MPLS circuits are manually configured (to hardwire to set paths), SD-WAN technologies have improved on this by integrating Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP). ZTP allows SD-WAN deployment and management to be controlled remotely through a centralised management system, therefore requiring less manual work to set systems up.
Finally, SD-WAN also introduces many additional security features that are not present in base setups of traditional WAN services, such as encryption, firewalls and intrusion prevention. Previously, with traditional WAN, these functions would require an additional appliance to be used within the system, however by integrating these into SD-WAN, there is now the ability to use a centralised configuration system for monitoring, troubleshooting and setting network-wide policies that are consistent across all devices, whilst also saving on initial outlay (as additional appliances are no longer required).
SD-WAN vs Traditional WAN Feature Comparison
| wdt_ID | wdt_created_by | wdt_created_at | wdt_last_edited_by | wdt_last_edited_at | SD-WAN | Traditional WAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:53 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:53 PM | Uses multiple transport services including broadband Internet, MPLS, LTE, amongst other formats. | Relies primarily on expensive private MPLS circuits. |
| 2 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:53 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:53 PM | Dynamically routes traffic across the best available path based on real-time network conditions and application requirements. | Uses static routing configurations over dedicated circuits with limited ability to adapt. |
| 3 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:53 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:53 PM | Offers centralised configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting through software-defined policies. | Requires complex and time-consuming manual management of proprietary hardware at each site. |
| 4 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:53 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:53 PM | Provides application-aware traffic steering and prioritisation to optimise performance. | All traffic must be routed via data centres, leading to additional latency and poor cloud app performance. |
| 5 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:53 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:53 PM | Includes built-in encryption alongside additional security functionality. | Lacks security features and so relies on a separate security stack. |
| 6 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:53 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:53 PM | Reduces costs by using broadband and allowing for software-based management. | Expensive due to reliance on MPLS and single-function hardware appliances. |
| 7 | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:53 PM | hyelland | 28/10/2024 02:53 PM | Enables deployment and management through zero-touch provisioning. | Requires manual configuration of the hardware. |
| SD-WAN | Traditional WAN |
Challenges and Considerations
Prior to implementing SD-WAN, it is important for IT decision makers to ensure adequate network infrastructure is in place. By ensuring the reliability of available routes (broadband, LTE, cloud connections and MPLS circuits) and understanding the limitations of the network (such as Service Level Agreements with network providers), it highlights weaknesses in infrastructure and shows paths that could be prioritised for crucial applications. This will also highlight redundancy and failover paths in order to maintain the system availability.
Once the network infrastructure has been properly evaluated, it is important to consider the different SD-WAN vendors as these will not only provide solutions with different features but these will also integrate differently depending on network infrastructure/cloud environments. As an example, it should be noted that some SD-WAN vendors provide solutions that primarily specialise in harnessing LTE connections, whereas others may specialise in broadband connections. These key differences help distinguish SD-WAN vendors and indicates the correct solution for your use case. The 2024 Netify best SD-WAN vendor article is a great way to find more information on vendors for your specific use case.
The level of access/control that administrators require over the service will also affect the SD-WAN infrastructure required and therefore it is important to make sure that any required centralised management, monitoring and analytics capabilities provided by the solution meet your requirements. Current solutions offer a range of control, from out-of-box to advanced, granular setting configurations, there is a specific solution for every use case.
Once the level of control has been initially identified, it’s important to prepare common practices and processes to ensure that any changes to configurations, software updates or troubleshooting follows the same format. These policies not only help maintain reliability and security of the platform once deployed but may also indicate if a higher/lower level of access and control over the system is required.
To further enhance the reliability and security of the service, IT decision makers should also consider the integration of features (such as encryption, firewalls and threat detection) within the context of the organisation’s security policies and regulations. It is also important for businesses to consider the time and resources to roll SD-WAN out across their sites as potential delays or outages may reduce the system’s reliability (at least in the short term).
By evaluating the potential challenges, IT decision makers can ensure deployment of their SD-WAN solution is based off careful considerations to produce a well-implemented network architecture, policies and the ability to outperform traditional WAN systems.
The Future of SD-WAN
Whilst SD-WAN has improved on traditional WAN systems by adding functions such as dynamic real-time routing, built in security systems and Zero Touch Provisioning; as SD-WAN is being increasingly used by businesses worldwide, the technology is growing in several additional areas:
- As more businesses move towards the cloud, so are the prevalence of cloud-based SD-WAN services. This has enabled services to integrate the cloud to create high-performances from the cloud to their applications for increased accesibility and reliability of the network. SD-WAN providers are improving on this by offering cloud-managed/cloud-hosted SD-WAN solutions therefore removing the need for physical SD-WAN appliances to be setup on physical premises.
- SD-WANs are leveraging AI and machine learning to optimise network performance, automate tasks and enhance security monitoring. This will improve overall network performance and increase reliability.
- There is a greater emphasis on advanced security features such as SASE (Secure Access Service Edge), firewalls and VPNs. By placing a greater emphasis on security features, SD-WAN solutions simplify system architecture, providing greater control over system access.
These features will extend SD-WANs capabilities and further improve it against traditional WAN systems. If your system is still using a traditional WAN system, we would recommend reading the 2024 Netify best SD-WAN vendor article to find out more information on vendors for your specific use case.


